




Why Do We Need Bones and Muscles?
The bones and muscles of the human body are what brick and cement are for a building. They help in our structural organization and movements.
Imagining yourself to be a clump of muscles and tissue without bones or the muscular framework must be a morbid view.
It is interesting to note that we are made up of around 206 bones and almost thrice the number of muscles, a whopping 600! We’ll look into the longest muscle in the human body, bones, and the list goes on. Let’s jump right in.
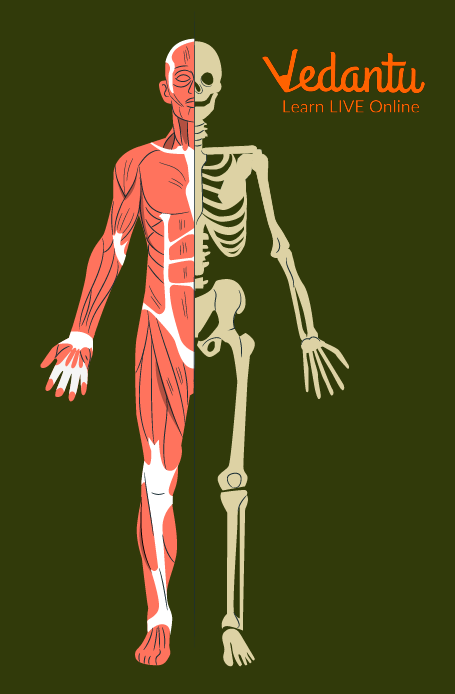
Bones and Muscles of Our Body
The Human Skeletal System
Let’s first understand the definition of the skeletal system. All the bones present in your body along with supporting structures like the tendons, ligaments, cartilages, and other connective tissues can be collectively called the skeletal system.

Skeletal System
Components of Skeletal system
Apart from bones, several parts also help the effective functioning of the skeletal system. These include the following:
Tendons (connective tissue connecting a muscle to a bone).
Ligaments (connective tissue connecting two bones).
Cartilage (coating which prevents friction at joints).
Joints (a structure where bones meet).

Tendon, Ligaments and Cartilage Present in a Join
Types of Bones
There are 206 bones present in the body that are classified on various bases. Some of these include based on function, shape, location, etc.,
Based on the Location
Axial skeleton (axial meaning forming the main axis) eg., brain and vertebrae.
Appendicular skeleton (appendicular meaning projecting from the axis) eg., bones of arms and legs.

Types of Bones (Based on Location and Shape)
Based on Shape
Long bone (eg., thigh bone)
Short bone (eg., bones of fingers)
Irregular bone (eg., vertebrae)
Flat bone (eg., knee-cap bone)
Round bone (eg., knee bone)
Functions of Bones
It gives a proper framework to our body.
It supports the weight of our body and helps us move around along with tendons and ligaments.
It acts as a storehouse of important nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and Vitamin D.
It helps the production of blood cells like the red and white blood cells in the bone marrow
It protects vital organs like the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, etc.
It also helps store and obtains fats as per the needs of the body.

Function of Bones
How to Maintain Bone Health?
It is important to take good care of our bones and supporting structures for healthy living. Some ways are:
Regular exercise.
Drinking plenty of water.
Consume green leafy vegetables and milk to ensure the required nutrients.
Getting the required amount of Vitamin D (morning and evening sunlights are the best sources of vitamin D).
Muscular System
Your body is made up of around 600-650 muscles which have a very versatile function to play. They help perform varied tasks. All these muscles bring about the muscular system of our body.

Muscular System of the Body
Types of Muscles
Muscles are classified as follows based on their function:
What is a Skeletal Muscle? These muscles are voluntary in control, meaning you can move and rest these muscles as per your will. Skeletal muscles are present close to your bones. They help with posture, movement, balance, weight-bearing, etc. These are also called ‘voluntary muscles’ as they are under voluntary control. The longest skeletal muscle in human body is placed in your thigh
What is a Smooth Muscle? These muscles are involuntary in control, meaning you cannot move and rest these muscles as per your will. They are present inside vital organs like the stomach, uterus, etcThey bring about digestion, excretion, etcThese are also called ‘visceral muscles’ as they are related to organs.
What is a Cardiac Muscle? The hero of organs, the heart has a special type of muscle itself named after it. These muscles are involuntary in control, and they are involved in the contraction and relaxation of the heart. They play an important role in blood circulation.

Types of Muscle Tissue
Functions of Muscles
Muscles are so versatile in function. They help in all the processes of the body. Some of these are listed below:
Breathing
Digestion
Removal of wastes
Movements
Posture
Circulation
How to Maintain Muscle Health?
It is necessary to take care of our muscular health. Some of the ways are :
Drinking plenty of water.
Regular exercise.
Eating a balanced diet.
Getting enough sleep, etc.
Summary
Let’s quickly brush through what we’ve learned up until now.
Bones and muscles are important components of our body helping our movement, posture, and several other life processes. Bones and other parts comprise the skeletal system which forms the major framework of our body. Other components of Bones include tendons, cartilages, ligaments, and joints.
Muscles provide support for movement and posture forming the muscular system of our body. They are vital parts of our body performing various functions from digestion, breathing, and pumping of blood. Primarily muscles of our body are of 3 types- Cardiac, Skeletal, and Smooth muscles.
FAQs on Bones and Muscles - Structures that Makes us Human
1. What do the bones and muscles in our body form together?
Together, the bones and muscles form the musculoskeletal system. The bones create a supportive framework called the skeleton, while the muscles attach to these bones to enable movement. This system is what gives our body its shape, allows us to stand and move, and protects our vital internal organs like the brain and heart.
2. What is the human skeleton and what are its main functions?
The human skeleton is the internal framework of the body, consisting of 206 bones in an adult. Its primary functions are crucial for our survival and daily activities:
- Support: It provides a rigid structure that supports the entire body and gives it its shape.
- Protection: It acts as a shield for delicate internal organs. For example, the skull protects the brain, and the rib cage protects the heart and lungs.
- Movement: Bones act as levers that muscles pull on to produce movement.
- Storage: Bones store important minerals, especially calcium.
3. How do bones and muscles work together to help us move?
Bones and muscles work in pairs to create movement. Muscles are attached to bones by strong tissues called tendons. To move a body part, a muscle must contract, or shorten. This contraction pulls on the bone it's attached to, causing it to move at a joint. Importantly, muscles can only pull; they cannot push. Therefore, they work in pairs. For example, to bend your elbow, your biceps muscle contracts, while your triceps muscle relaxes. To straighten it, the opposite happens.
4. What are joints and why are they so important for the body?
A joint is a place in the body where two or more bones meet. Joints are essential because they provide flexibility and allow our rigid skeleton to bend and move in different ways. Without joints, our bodies would be stiff and unable to perform actions like walking, running, or even picking things up. For example, the hinge joint in your knee allows it to bend and straighten, while the ball-and-socket joint in your shoulder allows for circular motion.
5. Why are babies born with more bones than adults?
Babies are born with approximately 300 bones, which is nearly 100 more than the 206 bones in an adult. This is because many of a baby's bones are made of soft, flexible cartilage that hasn't hardened yet. As a baby grows, many of these smaller bones fuse, or join together, to form the larger, stronger bones of the adult skeleton. This process allows for incredible growth and development during early childhood.
6. What are the different types of muscles in the human body?
The human body has three main types of muscles, each with a specific function:
- Skeletal Muscles: These are the muscles attached to our bones that we control voluntarily to move our body, like when we walk or lift something.
- Smooth Muscles: These are involuntary muscles found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach and intestines. They work automatically without us thinking about them.
- Cardiac Muscle: This is a special involuntary muscle found only in the heart. It contracts to pump blood throughout the body.
7. What happens to our muscles if we don't exercise or use them regularly?
If muscles are not used regularly through physical activity, they can begin to weaken and shrink. This condition is known as muscle atrophy. It happens because the body follows a 'use it or lose it' principle. Without the regular stress of exercise, muscle fibres become smaller and less efficient, making physical tasks more difficult. This is why staying active is crucial for maintaining muscle strength and overall health.









