




Learn the Parts of Leaves for Kids
Plants are the most important part of our natural ecosystem. They are the only source of harnessing solar energy, utilising as well as storing it. Moreover, they are the main source of transferring this energy to the upper strata of the ecosystem. Although a plant has various parts specialised for carrying out various functions like roots, stems, flowers, etc., but the most important part for the maintenance of the plant's life and directly or indirectly ours too is the leaf.
You must be wondering how! How can a small, flat green structure be this important for everyone? And many more such questions. We will answer all such queries in this article.

Parts of a Plant
A single plant can have a large number of leaves on it. Every different plant has different types of leaves varying in shapes and sizes, but all of them have a similar primary structure. Below we will see the various parts of the leaves. Read ahead to know about leaves and their importance.
Parts of Leaf Structures
A leaf majorly consists of two parts namely- leaf lamina and petiole. Below is the diagram for the parts of leaf:

Parts of a Leaf
The above picture of the leaf indicates the various parts of a leaf for kids with a little visually understandable structure of those parts of leaves.
Leaf Lamina and Petiole
Lamina is also called a leaf blade and the petiole can also be called the leaf stalk.
The broad green part of a leaf is referred to as the lamina. Whereas, the thin cylindrical stalk by which the leaf is attached to the stem is known as “petiole”.
On the lamina part of the leaf, there is a mid-rib or main vein passing through the centre of the lamina. It gives rise to a large number of veins that spread throughout all the parts of the leaf.
Structure of Leaves
Stomata
Present as minute pores on the surface of a leaf, these are called stomata. Their functions are as follows:
(i) They allow gaseous exchange in and out of the leaf.
(ii) They also allow the movement of water vapour.
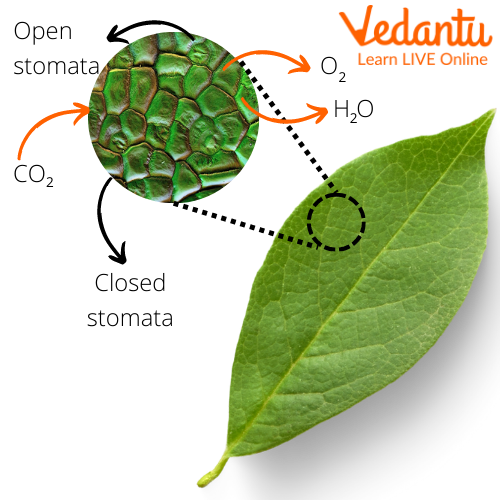
Stomata on the Leaf Surface
Chlorophyll
The leaves of a plant are usually referred to as the main food factory of the plant body due to the presence of stomata and specialised pigments that help in capturing sunlight and harnessing its energy to make food. This specialised green-coloured pigment is known as chlorophyll.
Functions of Chlorophyll Pigment
Chlorophyll imparts a characteristic green colour to the leaves and sometimes to the stem also.
Chlorophyll can harness light energy and can be used to prepare food in the form of starch for the whole plant body.
Major Functions of the Leaf
Leaves prepare food for the whole plant by the means of photosynthesis.
Leaves help to get rid of excess water from the plant through the phenomenon of transpiration.
Leaves also carry out the process of respiration for the plants.
Photosynthesis
Leaves perform a major function of synthesis of food in the plant by a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process in which plants make their own food using solar energy, carbon dioxide, and water.

Photosynthesis
During the Process:
Carbon dioxide is a gas needed in the process of making food by plants and is taken via the leaves from air and water and is carried into leaves from the soil through specialised vascular structures in the stem.
Sunlight provides a major source of energy for making food.
Chlorophyll helps in harnessing the energy from sunlight.
Oxygen gas is produced by the leaves during the process of photosynthesis as a by-product and is released out into the atmosphere.
The food produced by the leaves is in the form of glucose and then it is stored as starch.
Summary
In this article, we saw various parts of the leaves, parts of leaf structure, parts of a leaf, and their functions. The leaves of a plant are very important for the survival of a plant as well as for us humans. This is because plants during the process of photosynthesis release oxygen into the atmosphere, which is very essential for all living creatures; without oxygen our lives are not possible. We should all be thankful to plants and try to conserve them as much as possible.
FAQs on Different Parts of a Leaf and Their Functions
1. What are the main parts of a typical leaf?
A typical leaf consists of several key parts that work together. The main components are:
- Lamina: This is the broad, flat, green part of the leaf, also known as the leaf blade. It is the primary site for photosynthesis.
- Petiole: This is the stalk that attaches the lamina to the plant's stem. It helps to hold the leaf blade up to the sunlight.
- Midrib: The central, thick vein running down the middle of the lamina, providing support and transport.
- Veins: A network of smaller tubes branching out from the midrib that transport water, minerals, and food.
- Stomata: These are tiny pores, usually on the underside of the leaf, that allow for gas exchange (carbon dioxide in, oxygen out).
2. What is the primary function of a leaf for a plant?
The primary function of a leaf is photosynthesis. This is the vital process where the plant uses sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create its own food in the form of glucose (sugar). This process not only feeds the plant but also releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is essential for most life on Earth.
3. Why are most leaves green in colour?
Most leaves appear green because their cells contain a large amount of a green pigment called chlorophyll. This pigment is crucial for photosynthesis as its main job is to absorb energy from sunlight. Chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light very well but reflects green light, which is why our eyes perceive the leaves as green.
4. What is the importance of veins in a leaf?
The veins in a leaf are extremely important as they act as the plant's transport system and structural support. Their functions include:
- Transporting Water: They carry water and minerals from the stem to all cells in the leaf, which are needed for photosynthesis.
- Transporting Food: They carry the sugary food produced during photosynthesis away from the leaf to other parts of the plant for energy and growth.
- Providing Support: The network of veins forms a rigid skeleton that supports the leaf blade and keeps it flat to maximise sun exposure.
5. How does a leaf help a plant 'breathe'?
A leaf helps a plant with gas exchange, which is similar to breathing. This happens through tiny pores called stomata, mostly found on the leaf's underside. These stomata can open and close to control the flow of gases. They allow the plant to take in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis and release the waste product, oxygen. They also help the plant release excess water vapor in a process called transpiration.
6. Can leaves that are not green, such as red or purple ones, still perform photosynthesis?
Yes, leaves with colours other than green can still perform photosynthesis. These leaves contain other strong pigments, like anthocyanins (red/purple) or carotenoids (yellow/orange), that mask the green colour of chlorophyll. However, chlorophyll is still present and active underneath these other pigments, absorbing sunlight and making food for the plant.
7. What is the difference between the upper and lower surfaces of a leaf?
The upper and lower surfaces of a leaf are structurally and functionally different. The upper surface is typically darker, smoother, and waxier to maximise sunlight absorption and prevent water loss. The lower surface is usually lighter in colour and contains most of the stomata (pores). Placing stomata on the cooler, shaded underside helps the leaf exchange gases efficiently while minimising water evaporation from direct sunlight.









