




About : X-rays
X-rays are a type of radiation called electromagnetic waves that can be passed through our body. These rays cannot be seen by the naked eyes and we can't feel them. x-rays create pictures of the inside of the body. As these rays pass through our body, the energy which is stored in these x-rays is absorbed at different parts of the body. Let us learn more about x-rays and what do x rays show:

Chest x-ray
Discovery of X-rays
In 1895, a German physicist Wilhelm Rontgen discovered x-rays accidentally when he was testing whether cathode rays can pass through glass. The cathode tube was covered in heavy paper which was of black colour so he got surprised when he observed that an incandescent green coloured light escaped and projected on a nearby screen. Through experiments he found that the unknown light could pass through most substances and leave shadows of solid objects. He did not know what these rays were, so he named them ‘X’ meaning ‘unknown’ rays.

Wilhelm Rontgen - Physicist Who Discovered X-rays
Properties of X-rays
Let us discuss some properties of x-rays.
X-rays have very short wavelengths out of all from the electromagnetic spectrum.
These travel in a straight line and these do not carry an electric charge.
They do not require medium to travel; they can travel in vacuum.
They are highly penetrable.
These rays are diverging rays as they cannot be focused on a point.
How Do X-rays Work?
X-rays are produced when electrons of high velocity come to collide with the metal plates. During this process, they give out energy as x-rays and themselves are absorbed by the metal plate.
Firstly, the person is laid on an x-ray machine. The x-ray beam travels through the air and it comes in contact with the tissues of the body and then it produces an image on a metal film.
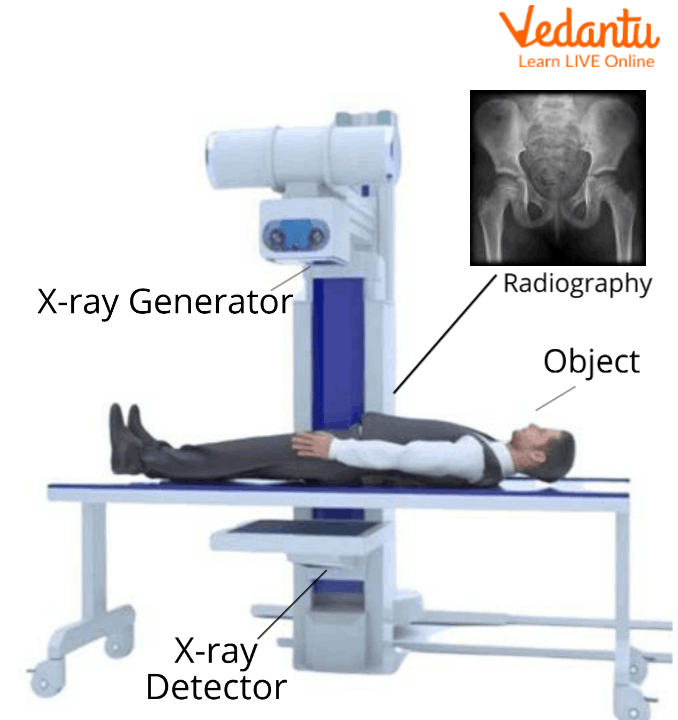
X-ray Machine
Soft tissues of the body like organs and skin cannot absorb the high velocity rays and the beam passes through them.
There are dense materials present inside our body for example bones, they can absorb the radiations of x-rays.
In the areas which are exposed to x-rays, they develop a film called x-rays film. White areas in the film show denser regions of the body for example bones which absorb x-rays and black areas on an x-ray show the soft tissues from which x-rays have not passed.

Exposure to x-rays
Uses of X-rays
X-rays have many uses. Some of these uses are listed:
Medical uses of x rays include detection of any breakage in bones of humans.

Bone x-ray
They work as scanners to scan the luggage of passengers in airports, rail terminals and many other places for security checking.
X-rays are emitted by celestial objects and are used to study and understand the environment.
It has industrial purposes also that is to detect any defects in the welds.
These are also used to restore old paintings.
Fun Facts About x-rays
Let us learn some xray facts for kids
In 1901, Wilhelm Roentgen's discovery earned him the Physics Nobel Prize.
The innovation of Wilhelm's spouse did not impress Wilhelm's wife. She spoke the words "I have seen my death" after witnessing the picture of her hand.
The invention of the X-ray by Wilhelm, who wanted everyone to profit from its use, resulted in several medical advancements.
The terms "X-ray" and "image" both describe the process used to obtain the image.
There are several variations to spell X-ray, including xray, X ray, X-ray, and x-ray.
Sample Questions
1. What are the most common types of x-rays?
Ans: The most common types of x-rays are chest x-rays, bone x-rays, hand x-rays, joint x-rays, dental x-rays and many more.
2. Why do x-rays take so long?
Ans: X-rays take a long time because we need to angle the body in different positions to see the different parts of the bones and joint spaces etc.
3. How many x-rays can you have in your lifetime?
Ans: An average healthy human can have as many x-rays as possible in his or her lifetime.
Summary
X-rays are radiations which have very short wavelengths and can be used to take pictures of the internal organs of the body. X-rays are used in many ways but the most important use of them is in the medical field as they are used to detect defects in internal organs for example bone x-rays can be performed to check fractures. Radiations have some limitations also as their high dosage causes cancer.
FAQs on How Do X-rays Work?
1. How do X-rays work in simple terms?
Think of an X-ray machine as a special camera. It sends a beam of high-energy waves, called X-rays, through your body. Dense parts of your body, like bones, block many of these rays, while softer parts like muscles and organs let more pass through. A detector on the other side captures the pattern of rays that get through, creating a shadow image. The white parts on an X-ray film are where the fewest rays reached the detector.
2. Why do bones appear white on X-rays, but soft tissues look grey or black?
This happens because of a property called density. Bones are very dense and contain elements like calcium, which are excellent at absorbing or blocking X-rays. Since very few X-rays can pass through bone to reach the detector, these areas appear white. In contrast, soft tissues like skin and muscle are less dense, allowing most X-rays to pass through easily, making them appear in shades of grey or black on the final image.
3. How does an X-ray machine actually produce X-rays?
Inside an X-ray machine, a filament is heated with electricity until it releases electrons. A very high voltage is then used to make these electrons accelerate and crash into a hard metal target. This high-speed collision releases a huge amount of energy in the form of X-ray photons. This beam of photons is then aimed at the part of the body being examined.
4. What kind of waves are X-rays?
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, similar to visible light, radio waves, and microwaves. The main difference is that X-rays have a much shorter wavelength and higher energy than visible light. This high energy is what gives them the ability to pass through materials that light cannot.
5. Are X-rays harmful, and are they safe for medical use?
X-rays use a very small amount of radiation. For a single diagnostic X-ray, the benefit of getting an accurate diagnosis is considered much greater than the tiny associated risk. However, very high doses or frequent exposure can be harmful to living cells. That's why doctors only order X-rays when necessary, and technicians always use the lowest possible dose needed to get a clear image.
6. What are some common uses of X-rays besides finding broken bones?
While famous for medical imaging, X-rays have several other important uses. These include:
- Airport Security: To scan luggage and cargo for prohibited items.
- Industrial Inspection: To find cracks or flaws in metal parts and welds without having to break them.
- Astronomy: To study high-energy objects in space, such as black holes and distant galaxies.
- Art History: To see underneath layers of paint to authenticate or study old paintings.
7. What materials can block X-rays?
X-rays can be blocked by materials that are very dense. The most common material used for protection is lead because its high density is very effective at absorbing X-ray photons. This is why you see technicians using lead aprons and standing behind lead-lined screens during an X-ray procedure.
8. Do you need to do anything special to prepare for an X-ray?
For most standard X-rays, like for a bone or chest, no special preparation is needed. However, for certain types of X-rays that examine the digestive system, you might be asked to fast (not eat or drink) for a few hours beforehand. It is always important to tell your doctor or the technician if you are, or might be, pregnant.









