
Which circuit will not show current in ammeter?
A.
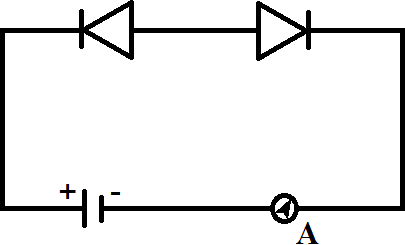
B.
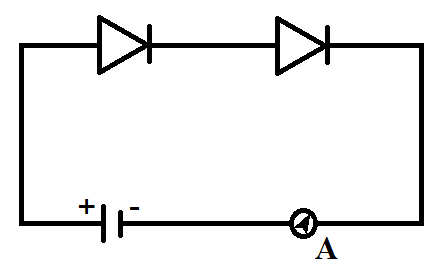
C.
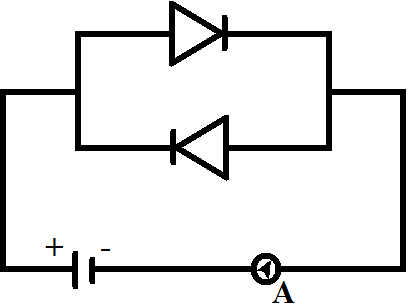
D.
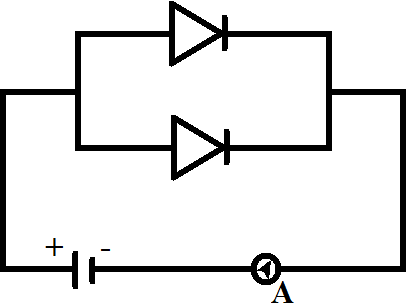
Answer
169.2k+ views
Hint:The pace at which electrons flow past a location in a complete electrical circuit is known as current. In general, current is equivalent to flow. The unit for measuring current is known as ampere (A).
Complete step by step solution:
We have to find which circuit will not show current in the ammeter for the given options. We can see that the circuit contains forward and reverse bias. Current always flows from forward bias, and no current flows from reverse bias. So, from bias we will identify that from which circuit current does not flow.
Case 1: If the biases are in series, both the biases should be forward, for the current to flow, otherwise no current will flow even if one of them is reverse biased.
For option A, we can see that the first bias, from which the current flows, is reverse and second is forward, so no current flows in circuit as one of them is reverse bias.
For option B, we can see that both the biases are forward bias so the current will flow from this circuit.
Case 2: If the biases are in parallel, as the current gets divided equally, so either one of the biases should be forward for the current to flow, otherwise no current will flow even if one of them is reverse biased.
For option C, we can see that the upper bias, from which the current flows, is forward and lower is reverse, so current flows in circuit as one of them is forward bias.
For option D, we can see that both the upper and lower bias are forward bias so the current will flow from this circuit.
So, option A is the circuit from which the current will not flow.
Note: The current always flows in a clockwise manner in the given circuits, from positive to negative, so according to that, identify which is forward and which is reverse bias. Moreover, a PN-junction diode is said to be in forward bias condition when the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the P-side of the diode and negative terminal to the N-side of the diode. In reverse bias condition, the positive terminal is connected to the N-side of the diode and negative terminal to the P-side of the diode.
Complete step by step solution:
We have to find which circuit will not show current in the ammeter for the given options. We can see that the circuit contains forward and reverse bias. Current always flows from forward bias, and no current flows from reverse bias. So, from bias we will identify that from which circuit current does not flow.
Case 1: If the biases are in series, both the biases should be forward, for the current to flow, otherwise no current will flow even if one of them is reverse biased.
For option A, we can see that the first bias, from which the current flows, is reverse and second is forward, so no current flows in circuit as one of them is reverse bias.
For option B, we can see that both the biases are forward bias so the current will flow from this circuit.
Case 2: If the biases are in parallel, as the current gets divided equally, so either one of the biases should be forward for the current to flow, otherwise no current will flow even if one of them is reverse biased.
For option C, we can see that the upper bias, from which the current flows, is forward and lower is reverse, so current flows in circuit as one of them is forward bias.
For option D, we can see that both the upper and lower bias are forward bias so the current will flow from this circuit.
So, option A is the circuit from which the current will not flow.
Note: The current always flows in a clockwise manner in the given circuits, from positive to negative, so according to that, identify which is forward and which is reverse bias. Moreover, a PN-junction diode is said to be in forward bias condition when the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the P-side of the diode and negative terminal to the N-side of the diode. In reverse bias condition, the positive terminal is connected to the N-side of the diode and negative terminal to the P-side of the diode.
Recently Updated Pages
Preparation of Hydrogen Gas: Methods & Uses Explained

Polymers in Chemistry: Definition, Types, Examples & Uses

P Block Elements: Definition, Groups, Trends & Properties for JEE/NEET

Order of Reaction in Chemistry: Definition, Formula & Examples

Hydrocarbons: Types, Formula, Structure & Examples Explained

Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Trends, Notes & FAQs

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2025 Session 2: Application Form (Out), Exam Dates (Released), Eligibility, & More

Uniform Acceleration

Electric field due to uniformly charged sphere class 12 physics JEE_Main

Displacement-Time Graph and Velocity-Time Graph for JEE

Atomic Structure - Electrons, Protons, Neutrons and Atomic Models

JEE Main 2025: Derivation of Equation of Trajectory in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Instantaneous Velocity - Formula based Examples for JEE

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Raoult's Law - JEE

Learn About Angle Of Deviation In Prism: JEE Main Physics 2025

Wheatstone Bridge for JEE Main Physics 2025




