




Introduction to Number Counting
Learning numbers is a fundamental skill that we begin learning in kindergarten. This is also utilised in everyday life. For example, counting the number of students in class, buying a number of chocolates, etc. So you were wondering, what is this number counting? Counting numbers are natural numbers that can be counted. They begin with 1 and continue as 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. We cannot count zero, hence it is not included in counting numbers. In this tutorial, we will learn more about counting numbers. In this article, we are going to learn about counting and why we need numbers.

Numbers
What is Counting?
The practice of expressing the number of components or objects that are presented is known as counting. Natural numbers that can be numbered and are always positive are included in the category of counting numbers.
Why Do We Need Numbers?
Numbers are necessary for everyday life because we must count the number of hours, days, money, and so on. Numbers can be numbered and written in words such as one, two, three, and four. They can be counted both forward and backward. We use skip counting, reverse counting, counting by 2s, counting by 5s, and many more techniques to count these numbers.
Uses of Numbers
Our lives depend heavily on numbers. In order to determine your daily allowance for your food, transport, and other expenses, you can use numbers in your daily life by phoning a friend or family member on your cell phone.
Anything using the concepts of proportion and percentage, such as cooking. weighing produce, meat, poultry, and other items in the market, moving between levels or locations in the building via elevators, examining the cost of things that are on sale in a mall, Inquiring about the Facebook post likes you received, changing the channel of your preferred TV programs, the amount of time you spent at work or in class.

Uses of Numbers in Daily Life
Number Names
A technique to express numbers is using a number name. There are terminologies used to describe numbers. Numbers in words have been taught to students in primary education. These are the cornerstones of mathematics. All students should know by heart the counting name of the numbers. They will be able to accurately spell all the numbers if they learn the names and their spellings. Children should be taught the names of the numbers 1 through 10, then on. All of the counting digits' names ought to be familiar to them. Let's examine the reading and writing of digits 1 through 10.
Number Names 1 to 10
Let's study numbers and the number system up to ten:
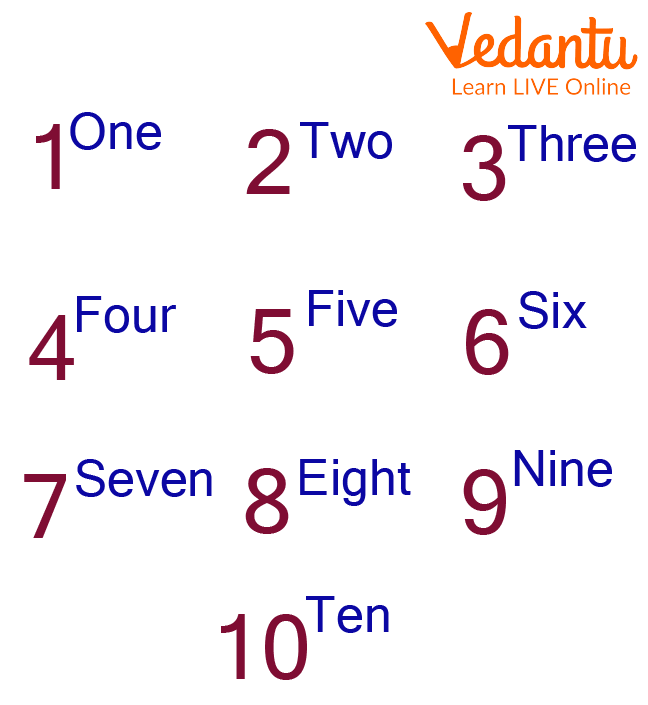
Number Names
Each learner must be able to identify the names of the numbers. These fundamental maths concepts will aid students in correctly spelling the numbers. Additionally, students may readily write such numbers when they attend lessons and learn how to do so from their teachers. Mathematics heavily relies on numbers. These numbers serve as the foundation for all mathematical and arithmetic processes, not just in lower-level courses but also in primary education.
Counting in Numbers with Hands
Using our hands and fingers, we can count from 1 to 10 as well. Visual maths is proven to hasten a child's mathematical development. The physical act of using hands and fingers connects numbers to their symbolic representation. Additionally, using this method will make it easier to recall the names of the numbers being tallied.

Counting Numbers with Hands
Solved Examples
Q1. Write the counting numbers from 1 to 20.
Ans: Counting numbers from 1 to 20 are as follows: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20.
Q2. Write the odd counting numbers less than 9.
Ans: Odd numbers are those numbers that are not divisible by 2. So, the odd counting numbers less than 9 are 1, 3, 5, and 7.
Q3. What are Counting Numbers Less than 10?
Ans: Counting numbers less than 10 can be listed as, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
Practice Problem
Q1. Write the Even Counting Numbers less than 12.
Ans: 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10.
Q2. Write the Odd Counting Numbers Between 6 and 16.
Ans: 7, 9, 11, 13, 15.
Summary
The term "counting numbers" refers to all natural numbers. These are always positive whole numbers, such as 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. Mathematical number systems depend heavily on the infinite counting numbers, which could be counted. The fundamental skill we begin learning in kindergarten is how to count. This is employed in daily life as well. Numerological examples can be found everywhere, even in daily life. the number of days in the year, the number of candies delivered to students in class, and so forth.
FAQs on Counting and Writing Numbers
1. What are counting numbers and why are they important in daily life?
Counting numbers are the numbers we use to count whole objects, starting from 1. They are also known as natural numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, and so on). They are important because they help us understand quantities in the world around us. For example, we use them to count how many apples we have, how many friends are in a room, or how many days are left until a birthday.
2. How do we write the numerals for the first twenty numbers (1 to 20)?
The numerals for the first twenty counting numbers are written in a specific sequence. They are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20. Each numeral represents a specific quantity.
3. How do you write the number names from one to twenty in words?
Writing numbers in words helps us learn their names and spellings. Here are the number names for 1 to 20:
- 1 - One
- 2 - Two
- 3 - Three
- 4 - Four
- 5 - Five
- 6 - Six
- 7 - Seven
- 8 - Eight
- 9 - Nine
- 10 - Ten
- 11 - Eleven
- 12 - Twelve
- 13 - Thirteen
- 14 - Fourteen
- 15 - Fifteen
- 16 - Sixteen
- 17 - Seventeen
- 18 - Eighteen
- 19 - Nineteen
- 20 - Twenty
4. Why is zero (0) not included when we start counting objects?
We don't include zero (0) when we count objects because counting begins with the first item, which we label as '1'. The number zero represents the concept of 'nothing' or the absence of any object. For instance, if you have no pencils in your hand, you have zero pencils. You can only start counting once you have at least one pencil.
5. What is the importance of learning numbers in the correct sequence or order?
Learning numbers in the correct sequence (1, 2, 3...) is crucial because the order gives numbers their value. It helps us understand that 5 is more than 4 and 9 comes before 10. This fixed order is fundamental for all future maths, including adding, subtracting, and understanding concepts like measurement and time.
6. Can you give some real-life examples of where we use counting every day?
We use counting constantly in our daily activities without even realising it. Some common examples include:
- At Home: Counting the number of plates to set on the dinner table.
- While Playing: Counting the number of players for a game or keeping score.
- At the Store: Counting coins to buy a candy.
- Time: Counting the seconds, minutes, or hours on a clock.
- Reading: Finding a specific page number in a book.
7. What is the difference between a number and a numeral?
A number is the actual idea or concept of a quantity. For example, the idea of having five fingers on one hand is a number. A numeral is the symbol we write down to represent that idea. For the number five, the numeral is '5'. So, the concept is the number, and the symbol is the numeral.















