




Introduction to Counting in 2s
Learning to add numbers by 2 is done through skip counting by twos. We begin by skip counting and adding when we first gain the concept of addition. Skip counting by 2 is adding 2 to each previous number to obtain the next number in the series. This method helps us in learning the concept of the addition of 2. Starting with 0, skipping counting by two results in a series that looks like $0, 2, 4, 6, 8$ and so on.
Skip counting is a mathematical strategy taught as a sort of multiplication. Earlier textbooks referred to this method as "counting by twos" (threes, fours, etc.). A person can count to ten using only the other even numbers $2,4,6,8$ and 10 when skip counting by 2s.
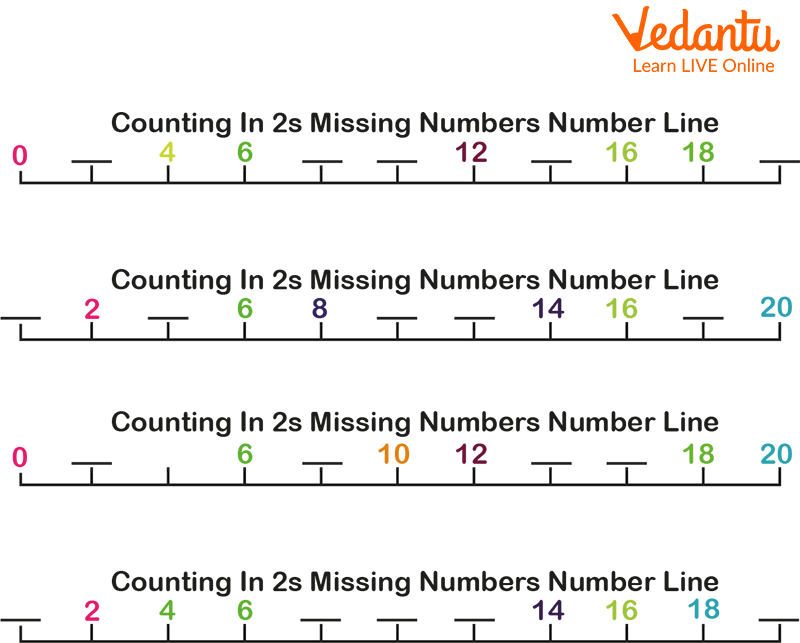
Counting in 2s
Counting in 2s
To skip count by two, add two to each previous number to get the subsequent number in the sequence. This skill helps in our understanding of the addition of two concepts. When learning addition by counting, skip counting by two is a highly helpful skill that advances our understanding of addition by adding two to each number. The table of two is easier to memorise when we skip count by two.
Skip Counting by 2 on Number Line
In this section, we will learn the concept of skip counting by 2 on a number line. We will make two jumps to reach one number to another. Let us have a look at the number line below. Starting from the number 0, when skip counting by 2, the next number will be 0 + 2 = 2.
So, we have landed on the number 2. Next, when we take another jump, we land on 2 + 2 = 4. Continuing in the same manner, we skip a number and land on the next number. So, the series continues like 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on.
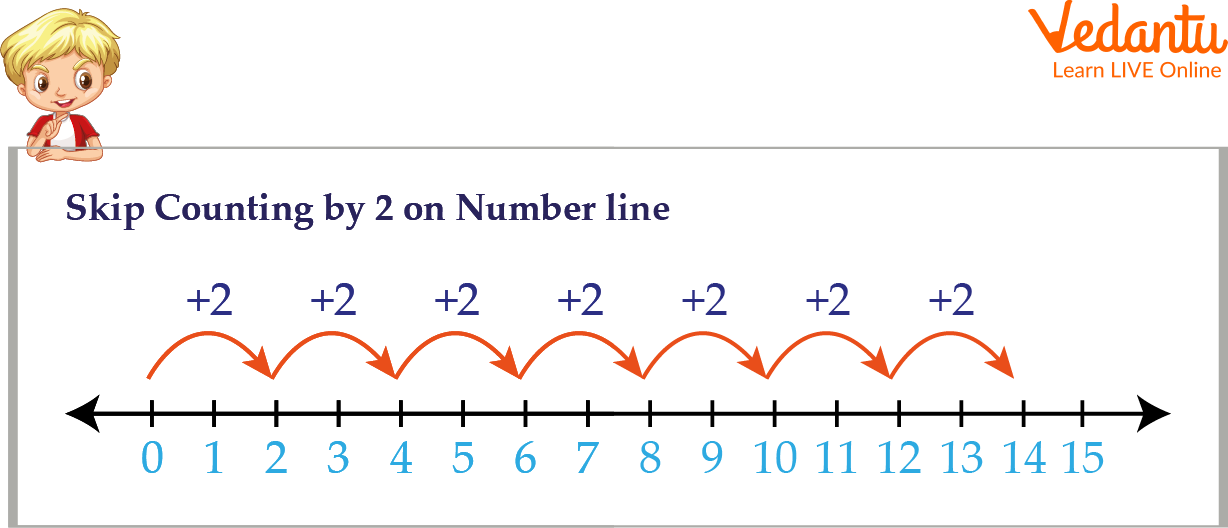
Skip Counting by 2 on Number Line
Find the missing numbers in the series 12, ___ , ___, 18, 20, 22, ___ using skip counting by 2.
Ans: To find the missing numbers by skip counting by 2, we add to each number in the series to obtain the next number.
12 + 2 = 14
14 + 2 = 16
22 + 2 = 24
So, the series is 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24
The missing numbers are 14, 16 and 24.
Example: Write the multiples of 2 up to 20.
Ans: We will use the method of skip counting by 2 to write the table of 2. The first multiple is 2, so we obtain the remaining multiples by adding 2 to each multiple.
2 + 2 = 4
4 + 2 = 6
6 + 2 = 8
8 + 2 = 10
10 + 2 = 12
12 + 2 = 14
14 + 2 = 16
16 + 2 = 18
18 + 2 = 20
So, the multiples of 2 up to 20 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20.
Counting in 2s Activities

Counting in 2s activities
Counting in 2s Game
Write all the multiples of two which are not circled.

Counting in 2s game
Ans: Multiple of 2s, which are not circled, are as follows:
2, 8, 24 and 30.
Counting in 2s Worksheet

Counting in 2s worksheet
Ans:

Summary
To conclude all the conceptual understanding regarding Counting in 2s in this article, we can say the idea of skipping two numbers on a number line. To get from one number to another, we have to make the jump of two. Then, later on, we saw some examples based on skip counting, like the missing number between the multiple of 2s. Also, to get more clarity on the topic, we have included the activity worksheet and games through which students will get more engaged with counting in 2s.
FAQs on Counting in 2s Missing Numbers Number Line
1. What is counting in 2s?
Counting in 2s, also known as skip counting by twos, is a method of counting where you add the number 2 repeatedly to get the next number in a sequence. Instead of counting every number (1, 2, 3, 4), you only say every second number. For example, if you start at 0, the sequence would be 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on.
2. How do you show counting in 2s on a number line?
To show counting in 2s on a number line, you make 'jumps' that are two units long. If you start at 0, you would jump over the number 1 and land directly on 2. From 2, you would make another jump, skipping over 3, to land on 4. Each jump represents adding 2, visually showing the pattern 0, 2, 4, 6, etc.
3. How can we find missing numbers in a sequence using counting by 2s?
To find a missing number when counting in 2s, you use a simple rule. If the blank is after a given number, you add 2 to that number. For example, in the series 12, __, 16, the missing number is 12 + 2 = 14. If the blank were before a number, you would subtract 2.
4. What are some real-world examples of counting in 2s?
Counting in 2s is very useful in everyday life. Here are a few examples:
- Counting pairs: When you count pairs of shoes, socks, or gloves, you are counting in twos.
- Even house numbers: Often, one side of a street has only even-numbered houses (e.g., 10, 12, 14).
- Counting money: If you are counting a stack of 2-rupee coins, you would count them as 2, 4, 6, 8 rupees.
5. What is the connection between counting in 2s and learning multiplication tables?
Counting in 2s is the first step to understanding multiplication. The sequence you get from counting in 2s (2, 4, 6, 8, ...) is exactly the same as the answers in the multiplication table of 2 (2x1=2, 2x2=4, 2x3=6, etc.). This helps children see that multiplication is just a fast way of doing repeated addition.
6. How does counting in 2s help in understanding even and odd numbers?
Counting in 2s provides a simple way to identify even numbers. Any number you land on when you start at 0 and count by 2s is an even number (e.g., 0, 2, 4, 6, 8). The numbers that you skip over are the odd numbers (e.g., 1, 3, 5, 7). This creates a clear pattern and a simple rule for distinguishing between the two types of numbers.
7. Can you count backwards in 2s on a number line? How does it work?
Yes, you can count backwards in 2s, and it is a great way to practise subtraction. On a number line, instead of jumping forward to add 2, you would jump backwards to subtract 2. For example, if you start at 20 and count backwards in 2s, your sequence would be 20, 18, 16, 14, and so on. Each backward jump is the same as taking away 2.









