




Essential Tools and Real-World Examples for Measuring Length
The term "length" refers to the size of an object or the distance between two points. The length of an object or the distance between two places is measured in length. It is used to determine the size of an object or the distance between two points.
In order to figure out what the basic length units are, we discover that there isn't one. This is because many measurement methods or systems are currently in use all over the world. However, the most commonly used length units today are US customary units and metric units, which include both SI and non-SI units. In addition, some countries continue to utilise British Imperial units. In this blog post, we'll be running through just a few of the most common units of measurement!
Units of Measurement List
There are two types of units of measurement:
Non-standard unit
Standard unit
Non-Standard Unit
Non Standard unit is one unit from units of measurement list. Children in Foundation Stage learn about measuring without needing to read any scales by using non-standard units.
The objective of non-standard measures is to focus the child on the concept of heavier, lighter, longer, shorter, etc. before they proceed onto the next step of measuring using standard units. Reading scales of any kind is a difficult ability in and of itself.
For example, in order to measure height, handspan or foot is used but all people don’t have equal length of hand or foot this implies getting a standard unit of measurement.

Non-standard Unit
Standard Unit
A common unit of measurement is a quantifiable language that makes the relationship between the item and the measurement clear to all parties.
In the US, it is measured in inches, feet, and pounds; in the metric system, it is measured in centimetres, metres, and kilograms.
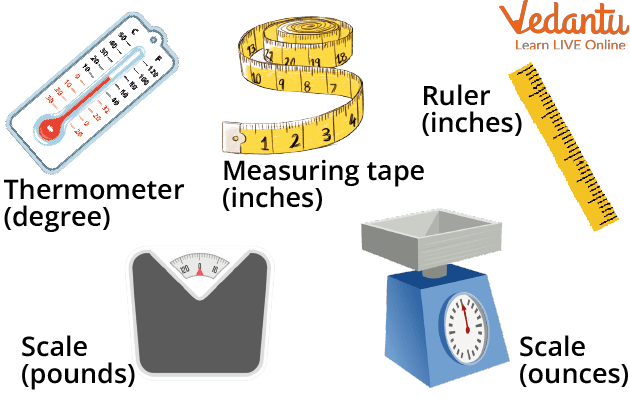
Standard Unit
For example, a ruler (used to measure height), measuring tape (used to measure length), scale (used for weight measurement), thermometer (temperature measurement), etc all are used to measure different types of things.

Non-standard Unit and Standard Unit
SI Unit of Length
The SI unit of length in the metric system is the metre.
The following are some of the other length units:
Kilometre
Hectometer
Decameter
Nanometer
Millimetre
Centimetre
Decimeter
Tools for Measuring Length
Tools help to get accurate measurements and this is the same for everyone at any place. A few tools that use for measuring length are:
Ruler
Scales
Measuring tape
Thermometer
Protractors
Order of Measurement
Small lengths (i.e. distances) are measured in cm and mm, while long lengths (i.e. distances) are measured in m and km. The 'Metre,' abbreviated as 'm,' is the standard unit of length.
One metre of length is divided into 100 equal parts. Each division is called a centimetre and is denoted by the letter 'cm.' As a result, 1 metre equals 100 centimetres.
The kilometre is the unit of measurement for the longest distance. One kilometre is divided into 1000 equal parts. A metre is the unit of measurement for each division. As a result; 1 kilometre equals 1000 metres.

Order of Measurement
Units of length and their counterparts, according to the length conversion charts, are:
1000 m = 1 kilometre (km) = 10 Hectometres (hm)
10 Decametres (dcm) = 100 Metres = 1 Hectometre (hm)
1 Metre (m) = 10 Decimetres (dm) = 100 Centimetres (cm) = 1000 Millimetres (mm)
10 Centimetres = 1 Decimetre (dm) (cm)
1 decimetre = 0.1 Metre
1 Centimetre (cm) = 10 Millimetres (mm) = 0.01 Metre
1 Millimetre = 0.001 Metre

Units of Length
Metric System
A metric system is a unit of measurement for distance, length, volume, weight, and temperature. There are many different types of metric systems. It is built on three fundamental units that can be used to measure practically anything in the world.
Kg- kilogram, used to measure the mass
S- second, used to measure time
M- metre, used to measure the length
L-litre used to measure the length

Basic SI unit
Types of Metric Systems
There are many different types of metric systems mentioned below;
1. SI System
The SI Units (Standard International System of Units) define the metre, kilogram, and second correctly.
2. CGS System
The CGS system of units is another system of expressing units in terms of length, weight, distance, and time.
3. Metric Units Smallest to Largest
Order of metric units smallest to largest: Nanometer, Millimetre, Decimeter, Metre, Decameter, Hectometer, Kilometre
Summary
Length measurement is used to determine an object's length or the separation between two locations. It is employed to calculate an object's size or the separation between two spots. US customary units and metric units, which comprise both SI and non-SI units, are currently the most widely used length units. Additionally, some nations still make use of British Imperial units. The yard is the basic unit of length in both the Imperial and United States customary systems. In 1799, the metric system was created. The metric system of units is consistent and logical. This is a big benefit for usage in the home, in education, in business, and in science.
FAQs on Units of Measurement in Maths: Length Explained
1. What exactly is length, and why is it important to measure it?
Length is a fundamental measurement that tells us how long an object is or the distance between two points. We measure length to understand and describe the world around us. For example, we need to know the length of a cloth to make a dress, the length of a room to buy a carpet, or the distance to a school from home. Without measuring length, we couldn't build things accurately, travel effectively, or even play sports with fair rules.
2. What are the most common units used to measure length in the metric system?
The metric system is a decimal-based system used worldwide for measurement. The most common units of length, from smallest to largest, are:
- Millimetre (mm): Used for measuring very small lengths, like the thickness of a coin.
- Centimetre (cm): Used for measuring smaller objects, like the length of a pencil or a book. 10 mm make 1 cm.
- Metre (m): The standard unit of length, used for measuring larger spaces like the length of a room or a playground. 100 cm make 1 m.
- Kilometre (km): Used for measuring long distances, such as the distance between two cities. 1000 m make 1 km.
3. What is the difference between standard and non-standard units of length?
The main difference is consistency. Standard units, like the metre or centimetre, have a fixed, universally accepted value. A metre is the same length everywhere in the world. In contrast, non-standard units, such as a handspan, footstep, or cubit, vary from person to person. While useful for quick estimates, they are not reliable for precise or scientific measurements because one person's handspan is different from another's.
4. How do you convert metres to centimetres and vice versa?
The conversion between metres (m) and centimetres (cm) is based on the relationship 1 metre = 100 centimetres. To convert:
- Metres to Centimetres: Multiply the number of metres by 100. For example, 5 metres is equal to 5 x 100 = 500 centimetres.
- Centimetres to Metres: Divide the number of centimetres by 100. For example, 250 centimetres is equal to 250 ÷ 100 = 2.5 metres.
5. Why is the metric system considered easier for length calculations?
The metric system is based on powers of 10, which makes calculations very straightforward. Every unit is a multiple or fraction of another by 10, 100, 1000, etc. This means you can convert between units simply by multiplying or dividing by these numbers, which often just involves moving the decimal point. This is much simpler than systems like the imperial system, where you have to remember irregular conversions (e.g., 12 inches in a foot, 3 feet in a yard).
6. Can you give real-world examples of when to use mm, cm, m, and km?
Choosing the right unit makes measurement practical. Here are some real-world examples:
- Millimetres (mm): A carpenter might measure the thickness of a plywood sheet in mm. A scientist might measure the size of an insect in mm.
- Centimetres (cm): You would measure your height, the length of a notebook, or the width of a table in cm.
- Metres (m): The length of a classroom, the height of a building, or the distance of a short running race (like a 100 m dash) are all measured in metres.
- Kilometres (km): This unit is used for long distances, like the distance you travel in a car from one city to another or the length of a river.
7. How did people measure length accurately before standard units like the metre were invented?
Before the invention of standard units, people relied on non-standard units, often based on the human body. These included the cubit (the length from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger), the handspan (the distance across an open hand), and the foot (the length of a person's foot). While these were useful for a single person or community, they caused confusion in trade and construction between different groups. To create consistency, rulers or kings would sometimes declare their own foot or arm as the 'standard' for their kingdom.
8. What is the standard international (SI) unit for measuring length?
The standard international (SI) unit for measuring length is the metre (m). It was established to create a single, consistent unit for scientific and general use across the globe. All other metric length units, like the centimetre and kilometre, are derived directly from the metre, making it the foundational unit of the entire system.















