Class 12 physics Chapter 9 Notes on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - Download FREE PDF



FAQs on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 Notes: CBSE Physics Chapter 9
1. How do Class 12 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments revision notes support fast and effective exam preparation?
Revision notes for Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 condense complex topics into concise summaries, allowing students to quickly review the core principles of image formation, reflection, refraction, and optical instruments. This targeted approach helps reinforce essential formulas, highlight key diagrams, and clarify sign conventions, making last-minute revisions simpler and more structured before exams.
2. What key concepts should I focus on when revising Ray Optics and Optical Instruments for Class 12?
While revising this chapter, pay extra attention to concepts such as reflection and refraction of light, total internal reflection, image formation by mirrors and lenses, lens and mirror formulas, sign conventions, power of a lens, and functioning of optical instruments like microscopes and telescopes. Practice applying formulas to problems and interpreting ray diagrams, as these are frequently tested areas.
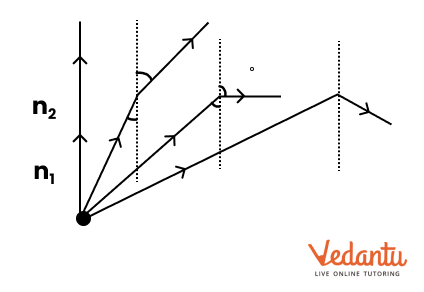
3. Why is mastering ray diagrams important for Ray Optics in Class 12 Physics?
Ray diagrams are vital in Ray Optics because they visually demonstrate how light interacts with mirrors and lenses to form images. Correctly drawn diagrams help in:
- Predicting image position, size, and nature (real or virtual)
- Clarifying the application of sign conventions
- Supporting answers in both theory and numericals
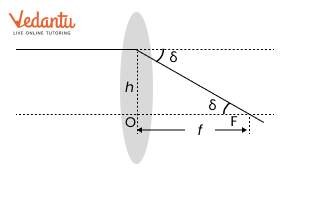
4. How can understanding the lens maker’s formula be beneficial during board revision?
The lens maker’s formula connects the focal length of a lens to the refractive index of its material and the curvatures of its surfaces. Mastering this allows students to:
- Calculate the focal length for different lens materials and shapes
- Solve numericals on combinations of lenses and instrument design
- Relate theoretical knowledge to the construction of optical devices
5. What is the significance of total internal reflection in Ray Optics and real-world applications?
Total internal reflection occurs when light passes from a denser to a rarer medium at an angle greater than the critical angle, causing it to reflect entirely within the denser medium. This principle is fundamental in understanding phenomena such as the sparkle of diamonds, optical fibers in communication, and mirages observed in nature, making it a key topic in the chapter and real-life applications.
6. How do the concise revision notes help in connecting Ray Optics concepts to optical instruments?
Revision notes bridge the gap between core light phenomena and the working of instruments such as eye, microscope, and telescope. They summarize how each device utilizes principles of reflection, refraction, and lens combinations, helping students understand both theoretical and practical design aspects essential for exams and future studies.
7. What practical strategies can be used to retain equations and principles during revision of Ray Optics?
Effective strategies include:
- Making a concept map of formulas for lenses, mirrors, and magnification
- Practicing derivations and their real-world interpretations
- Solving stepwise numericals with diagram support
- Quizzing with application-based questions
8. How does learning about sign conventions aid problem solving in this chapter?
Sign conventions in Ray Optics clearly dictate how to assign positive and negative values to distances and focal lengths for mirrors and lenses. Mastery reduces calculation errors, ensures consistency in applying mirror and lens formulas, and helps in interpreting the direction of image formation, which is necessary for both theoretical and practical exam questions.
9. In what ways do revision notes improve conceptual clarity in Ray Optics compared to textbook study alone?
Revision notes filter out non-essential details and present key points, formulas, and diagrams in a logical order, making it easier to see topic connections and revision flow. This streamlined approach supports memory retention, reduces confusion, and often includes solved examples tied to common exam questions, unlike standard textbooks.
10. How do the basic principles learned in Ray Optics Class 12 apply to advanced topics in later studies?
Fundamental concepts such as laws of reflection and refraction, lens and mirror equations, total internal reflection, and the behavior of light form the building blocks for advanced studies in wave optics, quantum optics, and optical engineering. A solid grasp at this level makes future topics like interference, diffraction, and optical instrument design much more accessible in higher classes and competitive exams.