




An Overview of Class 9 Chemistry Separation Of Mixtures Experiment
Introduction
One issue that arises regularly in chemistry is the separation of the mixture's constituent parts. Separation theory is based on the idea that elements in a mixture might have various physical and chemical characteristics. The constituents are unadulterated elements or compounds. Every sample of a pure substance has the same qualities under the same pressure and temperature conditions. Every sample exhibits the same melting point, boiling point, solubility in a specific solvent, etc. When two or more non-reacting chemicals are combined, the mixture's constituent parts preserve their own identities and attributes, and these properties are generally exploited for the separation of the mixture’s constituent parts.
Table of content
Aim
Separation of Camphor
Separation of Sand
Separation of Common Salt
Result
Aim
To separate the components of a mixture of sand, common salt, and camphor by sublimation.
Apparatus Required
Sand, common Salt (NaCl)
Camphor,
Filter Paper
Funnel
China Dish
Tripod Stand
Wire Gauze
Beaker
Glass Rod
Burner
Cotton Plug
Theory
Sublimation is defined as the conversion of a substance from the solid to the gaseous state without its becoming liquid
Camphor turns into vapour when heated. It is known as sublimation. Sand and regular salt, in comparison, do not sublime. So, by using the sublimation technique, camphor may be easily extracted from a combination that also contains ordinary salt and sand. Camphor vaporizes when heated, leaving the non-volatile components behind. Camphor turns from a liquid to a solid when it is cooled.
Solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent.
Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
Common salt is soluble in water, but sand is not soluble in water.
Sand particles stay on the filter paper when a mixture of common salt and sand in water is passed through the filter paper.
Evaporation is a technique used to separate out homogeneous mixtures.
Common salt can be extracted by evaporation from a solution of common salt in water.
Sublimation, filtration, and evaporation procedures are used to separate the various components of a mixture of camphor common salt and sand.
Procedure
1. Separation of Camphor
Place the sand, Camphor, and common salt combination in a China dish, then top it with an upside-down funnel.
Cover the funnel's opening with cotton.
Gently heat the China dish by setting it over a tripod stand.
Track the adjustments. Camphor is seen to go through sublimation, meaning that it produces vapours that condense on the funnel's cooler sides.
Remove the condensed camphor from the funnel's interior walls with a scraper.
Sand and regular salt are present in the mixture that does not sublimate and remains in the China dish.
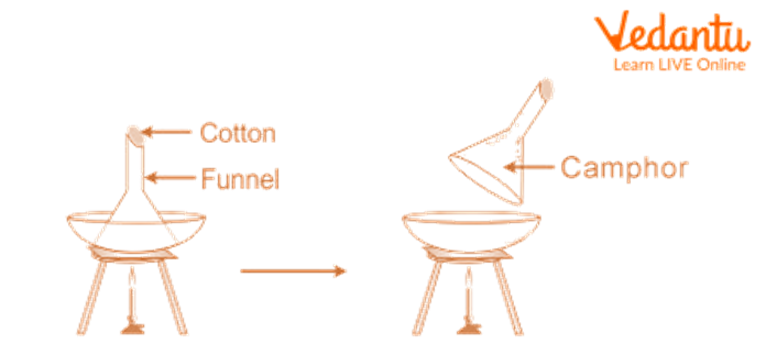
Separation of Camphor
1. Separation of Sand
Now, we will add water to the non-sublimate mixture.
Using a clean glass rod, stir the mixture.
Filter the mixture.
Sand is collected as the residue on the filter paper, whereas a common salt solution is obtained as the filtrate.
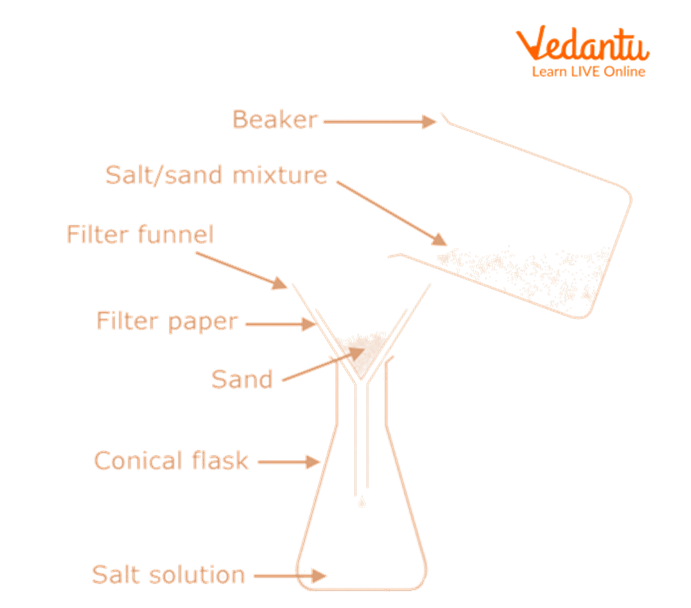
Separation of Sand
3. Separation of Common Salt
Take the filtrate and put it in a China dish.
Dry the filtrate to the point where sodium chloride (common salt), which is left behind as the water evaporates, is left in the China dish.
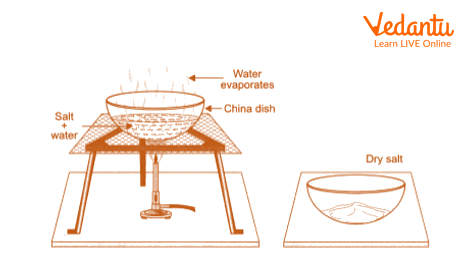
Separation of Salt
Observations
Result
Sublimation, Filtration, and Evaporation are used to separate the mixture of Camphor, sand, and table salt.
Precautions
Be careful during heating experiments.
Keep the flame low if you are using a Bunsen burner.
Be careful when heating camphor, as it is volatile.
Add a cotton plug to the funnel's end to prevent the escape of camphor vapours.
Take care while filtering so that the filter paper does not tear off.
Lab Manual Questions
1. In the experiment mentioned above, you saw the transformation of solids into vapours. Do you think this shift is physical or chemical?
Ans. Directly converting solids to vapours constitutes a physical change.
2. Can any method be used to separate a mixture's two water-soluble components? Justify your response.
Ans. It is possible to separate two components of a combination based on their different levels of solubility in water if they are soluble in water. The crystallisation will be the method used. Chromatography is an additional method that may be employed.
3. What factors, in your opinion, could cause some solids to convert directly to vapours or vice versa?
Ans. Some solids convert directly to vapours or vice versa. This is because of the solid's high vapour pressure in the liquid form. There is essentially no liquid state.
4. What would the separation process have been like if the mixture had been dissolved in water in the initial step?
Ans. Since both Camphor and sodium chloride are water-soluble, if the combination had been dissolved in water in the first stage, their separation would not have been possible.
Viva Questions
1. What do you understand about separation Techniques?
Ans. A mixture is made up of two or more different forms of matter that may be present in different proportions and that can be physically separated using techniques that separate the mixture's components based on their physical characteristics.
2. Why does the mixture need to be separated?
Ans. The mixture needs to be separated because
To remove the unnecessary components from a combination, various components of the mixture are separated.
To separate more than one useful component from a mixture.
To acquire pure materials.
For instance, grain bought in stores may come with a variety of contaminants, including bits of stone, husk, broken grains, etc.
3. What are the differences between Pure substance and mixture?
Ans. The differences between Pure substance and Mixture are as follows:
4. What type of mixtures are separated by the technique of crystallisation?
Ans. The types of mixtures that are separated by the technique of crystallisation are:
This method is used to separate a solid-liquid mixture.
When a solid is dissolved in a liquid, it can be separated from the mixture by evaporating the mixture that leaves behind crystals of the solid.
For instance, crystals of alum (phitkari) are separated from impure samples, and sea salt obtained from the sea is removed from impurities.
5. What do you mean by sublimation?
Ans. A substance can sublimate when it moves straight from the solid to the gas phase without first going through the liquid phase.
6. How will you separate sand and water from their mixture?
Ans. Filtering Technique: A filter paper is used to filter a sand and water mixture (a filter with very fine pores). The filter paper traps larger sand particles, separating them from the water.
7. Give two examples other than camphor, which undergoes sublimation.
Ans. Ammonium Chloride and Iodine are the two examples which undergo sublimation.
8. Is it possible to separate the mixture of Camphor and Naphthalene by sublimation?
Ans. No, it is not possible to separate the mixture of Camphor and Naphthalene by sublimation because both are sublimely solids, and they sublime on heating.
9. How to separate cream from milk?
Ans. By centrifugation technique, we can separate cream from milk.
10. What are the techniques used to separate the components of the mixture?
Ans. The techniques used to separate the components of the mixture are:
Evaporation
Distillation
Filtration or Sedimentation
Separating Funnel
Magnetic Separation
Practical Questions
A sample of a mixture that is heterogeneous is:
Oil in water
Sugar solution
Salt in water
Air
Ans. Oil in water is a heterogeneous mixture.
The following technique can be used to separate the salt and sand aqueous mixture.
Centrifugation
Evaporation
Sublimation
Filtration
Ans. Filtration is the technique that can be used to separate the salt and sand aqueous mixture
When water is dissolved with sodium chloride and ammonium chloride, and then filtered, the residue is.
Sodium Chloride
Ammonium Chloride
Both
None
Ans. When water is dissolved with sodium chloride and ammonium chloride, and then filtered, the residue is none.
How could salt, iron filings, and sulphur be separated from one another?
Magnet, dissolve in water, filter, crystallise.
Magnet, filter, decant, crystallise.
Dissolve in water, filter, crystallise, and decant.
Decant, crystallise, filter, dissolve in water
Ans. The magnet will separate the iron fillings from the mixture of salt and sulphur. Then we will dissolve the mixture in water and filter out the mixture using filtration technique. As a residue, we will get sulphur and salt solution as a filtrate. Follow up the crystallisation process and we will get the crystals of common salt.
Brine solution is
milk in water
an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide
a concentrated solution of sodium chloride
molten butter
Ans. Brine is a concentrated solution of sodium chloride
Name the material that sublimates and is used to protect warm clothes.
Ammonium Chloride
Iodine
Neem Leaves
Naphthalene
Ans. Naphthalene is the material that sublimates and is used to protect warm clothes.
Which one of the following is a pure compound?
Air
Crude oil
Sugar
Tea
Ans. Sugar is a pure compound
Common salt and water can be entirely separated using the procedure of
Filtration
Distillation
Evaporation
Centrifugation
Ans. Common salt and water can be entirely separated using the procedure of evaporation.
The components of the compound can be separated by using
Physical method
Chemical method
Cannot be separated by using any method
None of the above
Ans. The components of the compound can be separated by using the chemical method
An example of a homogeneous mixture is
Sugar Solution
Milk
Sand in water
Blood
Ans. Sugar Solution is an example of a homogeneous mixture
Conclusion
Separation techniques are those techniques that can be used to separate two different states of matter such as liquids and solids. Separation processes or a separation method or simply a separation is methodology to attain any mass transfer phenomenon that converts a mixture of substances into two or more distinct product mixtures. Separation is an important asset to purify components of interest from mixtures.
FAQs on Class 9 Chemistry Separation Of Mixtures Experiment
1. What are some important differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures that are frequently asked in Class 9 exams?
For your Class 9 Chemistry exam, it's important to distinguish between these two types of mixtures based on the following key points:
- Composition: A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout (e.g., saltwater), while a heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition where components can often be seen separately (e.g., sand in water).
- Visibility of Components: In a homogeneous mixture, the constituent particles are not visible to the naked eye. In a heterogeneous mixture, the components are often easily visible.
- Phase: The entire homogeneous mixture exists in a single phase. A heterogeneous mixture can consist of substances in two or more different phases (e.g., solid sand in liquid water).
2. From an exam perspective, why is crystallisation considered a better technique than simple evaporation for obtaining a pure solid?
Crystallisation is superior to evaporation for obtaining a pure solid for two main reasons often tested in exams:
- Purity: Evaporation removes the solvent completely, leaving behind both the desired solid and any soluble impurities. Crystallisation, however, forms pure solid crystals, leaving the impurities dissolved in the mother liquor.
- Decomposition: Some solids, like sugar, can decompose or get charred upon strong heating to dryness during evaporation. Crystallisation avoids this by using a saturated solution and gentle cooling, preserving the solid's chemical nature.
3. What is the principle of chromatography, and what are two of its important applications for the CBSE Class 9 syllabus?
The principle of chromatography is based on the differential movement of different components of a mixture through a stationary phase (like filter paper) under the influence of a mobile phase (solvent). Components that are more soluble in the solvent travel faster and farther up the paper.
Two important applications for your exam are:
- To separate different colours from a sample of ink.
- To separate and identify drugs or pigments from natural sources or biological samples.
4. How would you separate a mixture containing sand, common salt, and ammonium chloride? This is a high-order thinking question (HOTS) for your exam.
To separate this mixture, you would use a sequence of methods based on the unique properties of each component:
- Step 1 (Sublimation): Heat the mixture gently in a china dish covered with an inverted funnel. Ammonium chloride will sublime (turn directly into vapour) and solidify on the cooler walls of the funnel, separating it from the salt and sand.
- Step 2 (Filtration): Add water to the remaining mixture of sand and salt. The salt will dissolve. Pour the mixture through a filter paper. The insoluble sand will be left on the filter paper as residue.
- Step 3 (Evaporation/Crystallisation): Heat the filtrate (salt solution) to evaporate the water. You will be left with pure common salt. For a purer sample, crystallisation is the preferred final step.
5. Under what conditions is fractional distillation an important separation technique for Class 9?
Fractional distillation is an essential technique used to separate a mixture of two or more miscible liquids that have different boiling points. The critical condition is that the difference in their boiling points must be less than 25 K (or 25°C). If the difference is larger, simple distillation can be used. A key example is the separation of different gases from liquid air or the separation of crude oil into fractions like petrol and diesel.
6. Why can't a mixture of alcohol and water be separated using a separating funnel? Justify your answer.
A mixture of alcohol and water cannot be separated using a separating funnel because they are miscible liquids. This means they mix completely to form a single, homogeneous solution. A separating funnel works on the principle of separating immiscible liquids—liquids that do not mix and form distinct layers due to differences in their densities (e.g., oil and water). Since alcohol and water do not form separate layers, this method is ineffective.
7. What is the principle of centrifugation, and what is one daily-life and one industrial application important for exams?
The principle of centrifugation involves spinning a mixture at high speed. This forces the denser particles to settle at the bottom while the lighter particles stay at the top. This technique is used to separate fine suspended particles from a liquid.
Important applications include:
- Daily-Life: Separating cream (butter) from milk in dairies or at home. The lighter cream is separated from the denser milk.
- Industrial/Medical: Used in diagnostic laboratories for separating blood components (plasma and red blood cells) and for urine tests.






























