




An Introduction to the Human Nervous System for Kids
Have you ever wondered how humans are able to feel sensations, think, move, or even talk? We can perform all of these and many more such actions due to the nervous system. The Nervous system is responsible for allowing communication between various other organ systems and the brain.
In simple terms, the function of the nervous system is to carry messages throughout the body. It is one of the most complex organ systems in the human body; without it, no information from our surroundings or from within the body would be able to reach the brain. So without this system, we would be more or less like a vegetable!
The nervous system consists of 3 main components - The Brain, The Spinal Cord, and the Nerves. Do you wish to know more about these components? Then continue reading through the article.

Parts of the Nervous System
Parts of the Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into two parts:
The Central Nervous System
The Peripheral Nervous System
The Central Nervous System (CNS)
The central nervous system includes the brain and the spinal cord. It’s responsible for interpreting, combining, and gathering information from the entire body as well as coordinating activities throughout the body. It also controls our thoughts, emotions, behaviours, sensations, breathing, heart rate, digestion, etc. Let's talk about the two parts of the CNS.
Brain - The brain to the human body is what a CPU is like to a computer. It controls all functions in the body – from sensation (hearing, eyesight, smell) to emotions to motion to memory and intelligence. Specific portions of the brain are responsible for specific functions; however, some complex functions such as thinking, reasoning, etc. require multiple parts to work together. The brain has 3 parts:
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain

Anatomy of the Human Brain
Spinal Cord - The spinal cord runs from the end of the hindbrain to almost the end of the spine. It is responsible for connecting the peripheral nervous system to the brain. Aside from connecting the two systems, the spinal cord is also responsible for involuntary actions known as reflex actions.
Reflex actions are simply actions that take place without conscious thought. This happens when you see a fast-moving object coming toward you, and you immediately duck. These actions are involuntary and controlled by the spinal cord.
The Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves. Nerves are made up of multiple smaller units known as neurons. Neurons are the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons consist of the cell body, the dendrites, and the axon. The dendrite receives information from the muscle cell and transmits it to the axon, which transmits the impulse to the next neuron. Thus, the function of nerves is to carry information in the form of electric signals, known as neural impulses, from one part of the body to the other. There are two different types of nerves:
Sensory Nerves - These carry signals to the brain and the spinal cord from other parts of the body. They carry information from the senses, such as the sensation of touch, smell, pain, etc. These nerves are made up of afferent neurons.
Motor Nerves - These carry information from the brain to the rest of the body. They cause movement by controlling the muscles. They are made up of different neurons.
The peripheral nervous system is divided into two systems - Somatic and Autonomous.
Somatic - It is responsible for controlling voluntary actions such as jumping, walking, dancing, writing, etc.
Autonomous - The nerves in this system control involuntary actions, i.e., the actions we do not have to think about doing. They control functions like the release of enzymes during digestion, the release of hormones, the flight and fight response, etc. It contains two systems under it: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
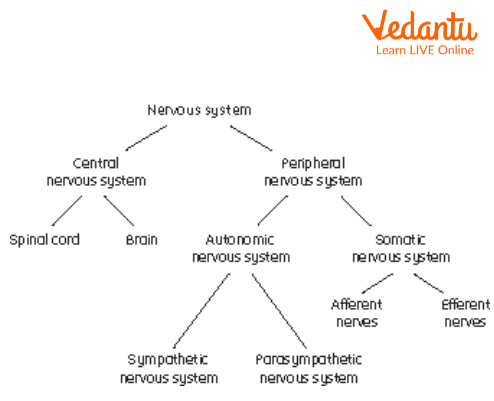
Flowchart of the Nervous System
Interesting Facts about the Nervous System
The human brain has almost 100 billion neurons that are connected to thousands of others, and it uses almost 20 percent of the total oxygen we breathe in.
As the nervous system is so essential, it is protected by three layers of membranes known as meninges, which contain cerebrospinal fluid between them.
For further protection, the brain is encased within the skull, and the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae of our spines.
Summary
The function of the nervous system is to allow communication between the organs and the brain as well as between our outside surroundings and the brain. The nervous system has two parts - the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
The CNS is divided into the brain and the spinal cord. Nerves make up the peripheral nervous system. The PNS is further divided into somatic and autonomic nervous systems. All these parts of the nervous system work in harmony to allow humans to function the way we do.
FAQs on What is the Nervous System?
1. What is the nervous system in simple terms?
Think of the nervous system as your body's main control centre. It is a complex network of nerves and specialised cells called neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is responsible for controlling all your actions, thoughts, and automatic responses to the world around you.
2. What are the main functions of the nervous system?
The nervous system has three primary functions that work together to keep you safe and responsive:
- Sensory Function: It gathers information from both inside and outside your body through sense organs.
- Integrative Function: It processes and interprets this sensory information to make decisions.
- Motor Function: It sends commands to your muscles, glands, and organs to carry out an appropriate response.
3. What are the basic building blocks of the nervous system?
The basic building block of the nervous system is a specialised cell called a neuron. Your body contains billions of them. Each neuron acts like a tiny wire, receiving signals through its dendrites and sending signals out through its axon. Together, they form the vast communication network that carries messages throughout your body.
4. What are the two major parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system is divided into two main parts:
- The Central Nervous System (CNS), which consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It acts as the body's primary processing and command centre.
- The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), which is made up of all the nerves that branch out from the CNS to the rest of the body. It connects the CNS to your limbs and organs.
5. What is the difference between the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems?
The main difference is their job. The Central Nervous System (CNS), which is just the brain and spinal cord, is the decision-maker. It receives information, figures out what to do, and gives the orders. The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), which includes all other nerves, acts as the messenger. It carries sensory information to the CNS and then carries the orders from the CNS back to the muscles and glands.
6. How does the nervous system send messages so quickly?
The nervous system sends messages using fast-moving electrical and chemical signals. An electrical impulse, called an action potential, travels down a neuron. When it reaches the end, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These chemicals jump a tiny gap to the next neuron, passing the message along in a fraction of a second.
7. Can you give an example of the nervous system in action?
A perfect example is when you accidentally touch a hot pan. Sensory nerves in your skin (PNS) instantly send a danger signal to your spinal cord (CNS). Without even waiting for your brain to process the pain, the spinal cord immediately sends a command back to your arm muscles to pull your hand away. This lightning-fast, automatic response is called a reflex arc.
8. Why is it so important to protect our brain and spinal cord?
The brain and spinal cord form the Central Nervous System (CNS), the command centre for your entire body. It controls everything from your heartbeat to your memories. Unlike other body cells, the neurons in the CNS have a very limited ability to heal or regrow if they are damaged. This is why an injury to these areas can have severe and permanent effects, and why they are protected by the hard bones of the skull and spine.





















