NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics- Chapter-wise FREE PDF Downloa
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics - Free Latest PDF (2024-25)
1. Why are NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics essential for the 2025-26 academic session?
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics are crucial as they provide a structured, step-by-step guide to solving all the problems in the textbook prescribed by CBSE for the 2025-26 session. They ensure students understand the correct methodology to apply concepts, which is vital for scoring well in school exams and building a strong foundation for competitive exams.
2. What chapters are covered in the NCERT Class 11 Physics Solutions?
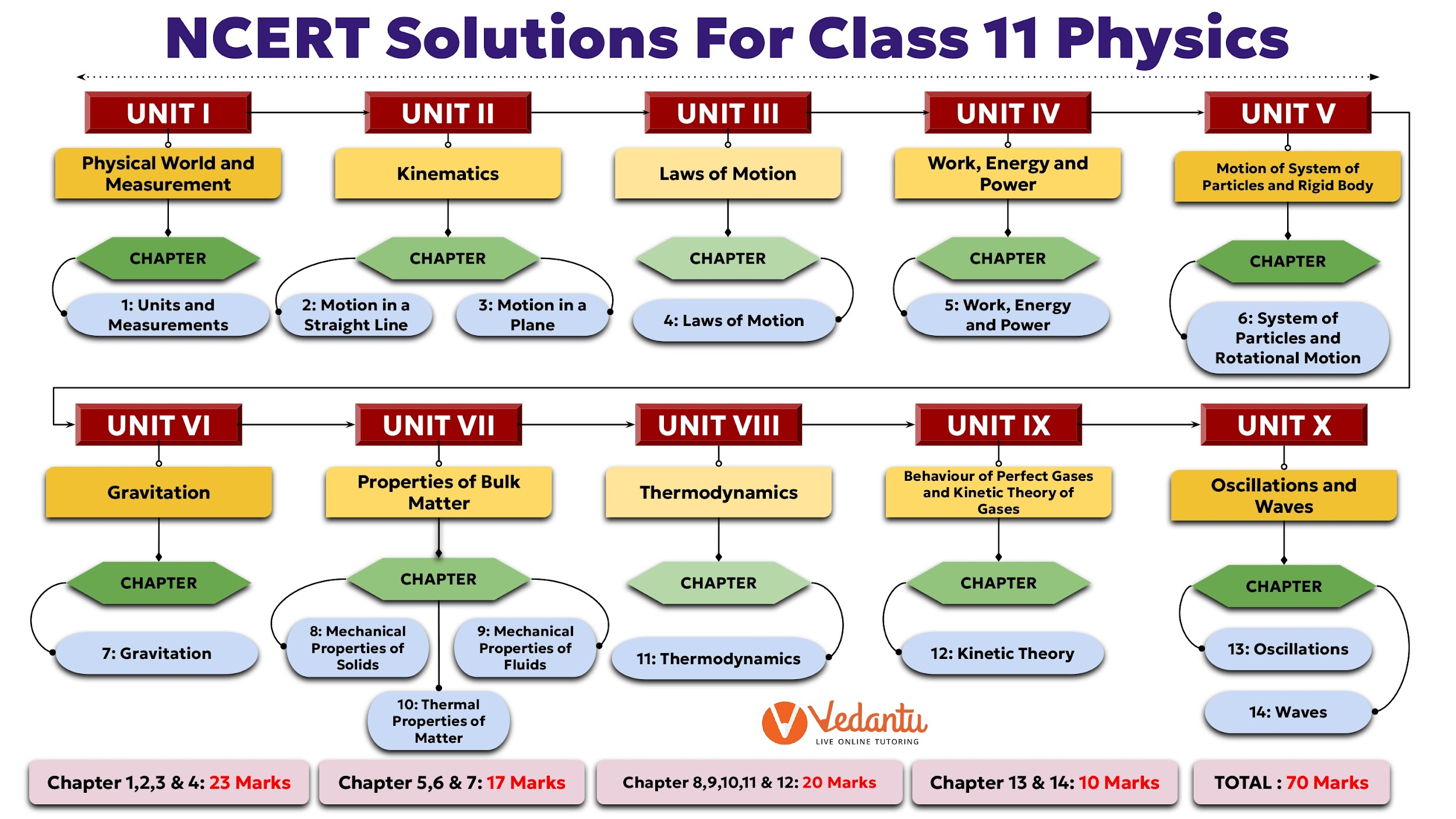
The solutions cover the entire syllabus, which is divided into two parts. Key chapters include:
- Part 1: Units and Measurement, Motion in a Straight Line, Motion in a Plane, Laws of Motion, Work, Energy and Power, System of Particles and Rotational Motion, and Gravitation.
- Part 2: Mechanical Properties of Solids, Mechanical Properties of Fluids, Thermal Properties of Matter, Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory, Oscillations, and Waves.
Solutions are provided for all in-text and exercise questions for each chapter.
3. How does following the step-by-step method in NCERT Solutions improve problem-solving skills?
The step-by-step approach is fundamental for building analytical skills. It teaches students to break down complex problems into manageable parts, identify the relevant physical principles and formulas, and apply them in a logical sequence. This methodical process minimises errors and is exactly what examiners look for when awarding full marks for method in board exams.
4. Do these solutions only provide the final answer or explain the concepts as well?
High-quality NCERT solutions do more than just provide an answer. They act as a learning tool by first stating the underlying principle or formula being used. This approach bridges the gap between theory and application, helping you understand *why* a particular method is used, thus reinforcing your conceptual understanding of the topic.
5. How can I use these NCERT Solutions most effectively for my studies?
For maximum benefit, you should first attempt to solve the NCERT textbook problems on your own. Afterwards, use the solutions to:
- Verify your final answer and method.
- Understand a more efficient way to solve the problem if you got it right.
- Identify your mistake and learn the correct steps if you got stuck or answered incorrectly.
This active learning approach is far more effective than simply copying the solutions.
6. Can mastering Class 11 NCERT Solutions help in preparing for competitive exams like JEE and NEET?
Absolutely. The Class 11 Physics syllabus forms the bedrock for competitive exams. By thoroughly working through the NCERT Solutions, you gain deep conceptual clarity and master the application of fundamental principles. This strong foundation is essential for tackling the advanced, multi-concept questions frequently asked in exams like JEE and NEET.
7. Are the NCERT solutions organised by chapter for easy access?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics are meticulously organised chapter-wise, following the exact sequence of the official NCERT textbook. Whether you are studying 'Thermodynamics' or 'Rotational Motion', you can easily find the detailed solutions for all the questions in that specific chapter, making your study process streamlined and efficient.
8. What common mistakes in Physics can be avoided by using NCERT Solutions?
By following the detailed steps in the NCERT solutions, students can avoid common errors such as incorrect sign conventions in vector problems, wrong unit conversions, or misapplication of thermodynamic laws. The solutions demonstrate the correct, structured way to present an answer, helping you identify and rectify these frequent pitfalls in your own work.