NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Lines and Angles Chapter 5 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles
1. What are the main topics covered in NCERT Class 7 Maths Chapter 5, 'Lines and Angles'?
Chapter 5, 'Lines and Angles', covers the foundational concepts of geometry. The NCERT solutions for the 2025-26 syllabus focus on the following key topics:
- Related Angles: This includes complementary, supplementary, adjacent, and vertically opposite angles.
- Linear Pair: Understanding two adjacent angles that form a straight line.
- Pairs of Lines: Concepts of intersecting lines and transversals.
- Angles Formed by a Transversal: Identifying corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and interior angles on the same side of the transversal.
- Transversal of Parallel Lines: Applying properties of angles when a transversal cuts through parallel lines.
2. How many exercises are there in Class 7 Maths Chapter 5, and what do they focus on?
The NCERT textbook for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 contains two exercises designed to build your understanding progressively.
- Exercise 5.1 has 14 questions that focus on identifying and calculating different pairs of angles, such as complementary, supplementary, and vertically opposite angles.
- Exercise 5.2 has 6 questions that test your understanding of the angles formed when a transversal intersects parallel lines.
3. What is the correct method to find the supplement of an angle, as shown in the NCERT Solutions?
According to the NCERT solutions, the correct and most direct method to find the supplement of any given angle is to subtract its value from 180°. The formula is:
Supplement = 180° – Given Angle
For example, to find the supplement of an 80° angle, you would calculate 180° - 80° = 100°.
4. How do the NCERT Solutions explain the process of finding an angle that is equal to its own complement?
The solutions guide you to solve this using a simple algebraic step-by-step method:
- Let the required angle be 'x'.
- Since it is equal to its complement, the complementary angle is also 'x'.
- The sum of two complementary angles is 90°.
- Therefore, the equation is: x + x = 90°.
- Solving this gives 2x = 90°, which means x = 45°.
Thus, 45° is the angle that is equal to its complement.
5. What key concepts must I know to solve the problems in Exercise 5.2?
To correctly solve problems in Exercise 5.2, you must have a clear understanding of the angle relationships that are formed when a transversal intersects two parallel lines. The key properties you need to apply are:
- Corresponding angles are equal.
- Alternate interior angles are equal.
- The sum of interior angles on the same side of the transversal is 180°.
6. Why is it impossible for two acute angles to be supplementary?
It is impossible because of their definitions:
- An acute angle is an angle that measures less than 90°.
- Two angles are supplementary if their sum is exactly 180°.
The sum of two angles that are each less than 90° will always be less than 180°. Therefore, two acute angles can never add up to 180° to form a supplementary pair.
7. How do the step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Chapter 5 help in preparing for school exams?
The NCERT Solutions for 'Lines and Angles' are structured to help with exam preparation by demonstrating the precise method for presenting answers. They teach you to state the theorems and properties (e.g., 'linear pair', 'vertically opposite angles') as reasons for each step in your calculation. This practice is crucial for scoring full marks in school exams, as teachers look for both the correct answer and the correct logical justification.
8. What is the main difference between adjacent angles and a linear pair?
While both involve angles next to each other, there's a key difference:
- Adjacent angles are any two angles that share a common vertex and a common arm but have no common interior points. Their sum can be any value.
- A linear pair is a special type of adjacent angle pair where the non-common arms form a straight line. The sum of angles in a linear pair is always 180°.
So, all linear pairs are adjacent angles, but not all adjacent angles form a linear pair.
9. Beyond just getting answers, how can I use these NCERT Solutions to build a strong foundation in Geometry?
To build a strong conceptual foundation, use the solutions as a verification tool, not a crutch. First, attempt to solve the NCERT exercise questions on your own. Then, use the detailed solutions to:
- Check your method: See if your approach matches the standard method.
- Understand the logic: Pay close attention to the reasoning provided for each step, which reinforces the underlying geometric properties.
- Identify weaknesses: If you get a problem wrong, the solution will help pinpoint the exact concept you misunderstood.























![Complement of \[20{}^\circ = 90{}^\circ -20{}^\circ =70{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/bc05539b-3566-4b65-82b4-202a5df72b7e_a..png)
![Complement of \[63{}^\circ =90{}^\circ -63{}^\circ =27{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/caa27bd5-5af0-4ceb-96d8-836f2a681a8f_b..png)
![Complement of \[57{}^\circ =90{}^\circ -57{}^\circ =33{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/69384ef8-b9d0-4a5f-a750-64752e6219ec_c..png)
![Supplement of \[105{}^\circ = 180{}^\circ -105{}^\circ =75{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/db6be495-b61c-4010-ba2d-0b8b182f820b_d..png)
![Supplement of \[87{}^\circ =180{}^\circ -87{}^\circ =93{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/9cc2cbc5-c305-4c3c-89dd-23aa276beba8_e..png)
![Supplement of \[154{}^\circ =180{}^\circ -154{}^\circ =26{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/3650506a-0a23-4a60-920f-d992f790a611_f..png)
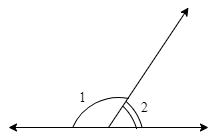
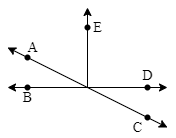
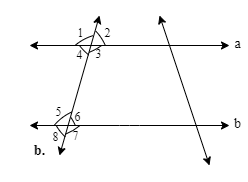
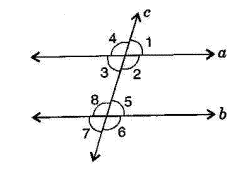
![\[(i)\] Given, \[l\parallel m\]and t is transversal line.](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/e7266142-03d5-4270-a31a-1792a17eab92_k..png)
![\[(ii)\] Given, \[l\parallel m\]and t is transversal line.](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/dbd25bac-0ddc-4f77-80f2-4902f501793f_l..png)
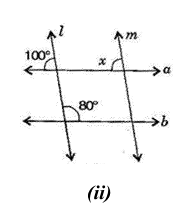
![\[(i)\] \[126{}^\circ +44{}^\circ =170{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/b94d9094-65ba-44f8-b5ed-23f17114abd7_n..png)
![\[(ii)\] \[75{}^\circ +75{}^\circ =150{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/b085cdc1-d512-48d5-8773-f6c8fab0cbe8_o..png)
![\[(ii)\] \[75{}^\circ +75{}^\circ =150{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/4d425726-1c3b-47b7-ba03-c598217b37dc_p..png)
![\[(iii)\]\[57{}^\circ +123{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/20b75529-9aac-45ac-a474-c34e2592a602_q%2C.png)
![\[(iv)\]\[98{}^\circ +72{}^\circ =170{}^\circ \]](https://elitestealsonly.com/seo/content-images/74604ab7-848d-40ba-a067-47f8f6aa7351_s..png)
