




Key Differences Between IgM and IgG Antibodies (Table & Functions)
The concept of Difference Between IgM and IgG is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively.
Understanding Difference Between IgM and IgG
Difference Between IgM and IgG is a foundational concept in immunology, especially for NEET aspirants. IgM (Immunoglobulin M) and IgG (Immunoglobulin G) are two major classes of antibodies found in the human body. These antibodies play different roles in the immune response. Understanding their structure, functions, and diagnostic significance is vital for solving MCQs and interpreting clinical scenarios in topics like immunology, serology, and human health and disease.
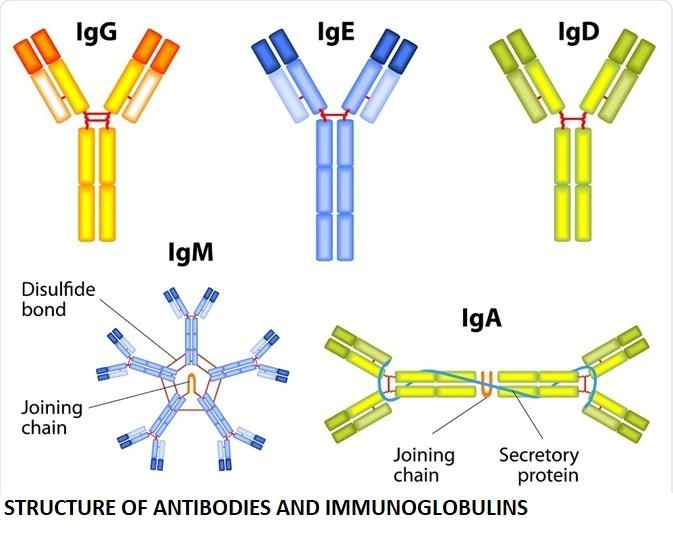
Key Differences Between IgM and IgG
Here’s a helpful table to understand the Difference Between IgM and IgG better, which is especially useful for NEET revision:
Difference Between IgM and IgG Table
| Parameter | IgM | IgG |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Immunoglobulin M | Immunoglobulin G |
| Appearance after Infection | First to appear (early responder) | Appears later (after IgM) |
| Duration | Short-term protection | Long-term protection |
| Structure | Pentamer (5 units joined) | Monomer (single unit) |
| Location | Mainly in blood and lymph | Blood, lymph, tissue fluids |
| Crosses Placenta | No | Yes |
| Percentage in Serum Antibodies | ~6-10% | ~75-80% |
| Diagnostic Significance | Indicates recent/active infection | Indicates past infection or immunity |
| Example Diseases | Rise in dengue/typhoid infection onset | Detected in later or recovered stage |
Key Functions and Easy Mnemonics
- IgM: Think “M = Main early responder” – Detects and fights new infections first.
- IgG: Think “G = Great guard lasting long & crosses placenta”.
Clinical and NEET Examples
Let’s look at real NEET-style clinical scenarios involving IgM and IgG:
- Dengue Serology: High IgM indicates fresh dengue infection; high IgG means past infection or immunity.
- Typhoid Tests: IgM positive = recent typhoid; IgG positive, IgM negative = old exposure.
- Prenatal Health: Only IgG can cross the placenta and protect the foetus, not IgM.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mixing up which antibody crosses the placenta (only IgG does).
- Thinking IgM gives long-term immunity (it is for early, short-term response).
- Assuming IgG always means current infection (it usually shows past/recovered infection).
Real-World Applications
The concept of Difference Between IgM and IgG is used in fields like medical diagnostics, vaccination, pregnancy care, and infectious disease control. Vedantu helps students connect these antibody classes to test result interpretation and the understanding of how our immune system responds to infections and vaccines in everyday life.
Practice Questions
- Which antibody indicates a recent infection in a patient’s blood test?
- Explain how IgG provides immunity to a newborn baby.
- Draw and label the structural difference between IgM and IgG antibodies.
- How does the presence of IgM vs IgG help diagnose dengue or typhoid?
In this article, we explored Difference Between IgM and IgG, its clinical importance, exam relevance, and how to link it with NEET question patterns. To learn more and build confidence, keep practicing with Vedantu and revise with quick comparison tables for similar topics.
Related Topics for Deeper Understanding
- Immunity
- Antibodies
- Immunoglobulin Structure
- Humoral Immunity
- Dengue
- IgG Test
- Types of White Blood Cells
- Vaccination
- Difference Between Antigen and Antibody
FAQs on Difference Between IgM and IgG for NEET
1. What is the difference between IgM and IgG in NEET?
In NEET, IgM and IgG are key immunoglobulins distinguished by their timing and function: IgM is the first antibody produced during a new infection providing short-term immunity, whereas IgG appears later and provides long-lasting protection. IgG can also cross the placenta to protect the fetus, unlike IgM. Understanding this helps answer MCQs on immune responses and serological testing.
2. Why is IgM called the “first responder” antibody?
IgM is called the first responder because it is the earliest antibody produced by the immune system upon encountering a new antigen. It is mainly found in blood and lymph and provides temporary protection until IgG antibodies form for long-term immunity.
3. What if IgG is positive and IgM is negative in reports?
A report showing IgG positive and IgM negative generally indicates past infection or immunity development, often from previous exposure or vaccination. It means the body has developed long-term protection, while there is no active or recent infection, which is marked by positive IgM.
4. What is the significance of IgG crossing the placenta?
The ability of IgG antibodies to cross the placenta is crucial as it provides passive immunity to the fetus. This protects the newborn from infections during the initial months of life until their own immune system matures.
5. How to remember IgM and IgG for NEET MCQs?
A simple mnemonic to remember IgM and IgG is: “M = Main early responder, G = Great guard lasting long.” This highlights IgM’s role in early immune response and IgG’s function in long-term immunity and placental transfer.
6. Why do students confuse IgM and IgG in NEET MCQs?
Students often confuse IgM and IgG because both are antibodies but differ in timing and function. Lack of clarity on which antibody indicates recent versus past infection, or misunderstanding placental transfer, leads to errors in MCQs. Using tabular comparisons and mnemonics can help resolve this confusion.
7. Can IgG appear before IgM after infection?
Typically, IgM appears before IgG during an immune response. However, in some infections or in vaccinated individuals, IgG may be detected earlier due to memory cells. For NEET, consider IgM as the marker of recent infection and IgG as indicate of past exposure or immunity.
8. Is IgM/IgG interpretation different in dengue and typhoid?
Yes, the interpretation of IgM and IgG varies with diseases like dengue and typhoid. In dengue, IgM indicates recent infection, while IgG shows past infection or secondary infection. In typhoid, presence of IgM suggests active infection, whereas IgG indicates exposure or immunity. Understanding these helps in clinical and NEET application questions.
9. How to avoid missing the “placenta” point in MCQs?
To avoid missing questions about placental transfer in NEET, remember IgG is the only immunoglobulin that crosses the placenta to provide passive immunity to the fetus. Using diagrams and focusing on this key distinguishing feature in revision helps retain this critical fact.
10. Do all antibody tests in biology mean the same in NEET?
Not all antibody tests are the same in NEET. Tests measuring IgM detect recent or active infections, while IgG tests indicate past infections or immunity. Different diseases have specific antibody profiles, so understanding the context and antibody types is essential for accurate interpretation of NEET questions.















