Electric Current and Its Effects: Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Question Answer - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Current and Its Effects
1. What are the key NCERT Solutions concepts covered in Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Current and Its Effects?
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 address concepts such as symbols of electrical components, electric circuits, heating and magnetic effects of electric current, construction and uses of electromagnets, and the functioning of electric bells, as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
2. How do you draw the circuit diagram for an electric circuit including a cell, bulb, and switch (as per NCERT Class 7 Science)?
To draw a circuit diagram as per NCERT Solution for Class 7 Science Chapter 10:
- Represent the cell with its symbol (longer line as positive terminal).
- Use a circle for the bulb, and a break in the line for a switch.
- Connect all symbols using straight lines to show the wires, placing the switch either open or closed depending on the situation.
3. What are the effects of electric current as per NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10?
Class 7 Science Chapter 10 describes two major effects of electric current:
- Heating Effect: When current flows through a conductor, heat is generated (e.g., in electric heaters).
- Magnetic Effect: Electric current produces a magnetic field (e.g., used in electromagnets and electric bells).
4. Why does a bulb in a circuit not glow even if the components are present (Class 7 NCERT Solutions)?
A bulb in an electric circuit may not glow if:
- The wire connections are loose or incomplete.
- The cell is exhausted or dead.
- The bulb is fused or defective.
- The switch is not in the 'ON' position.
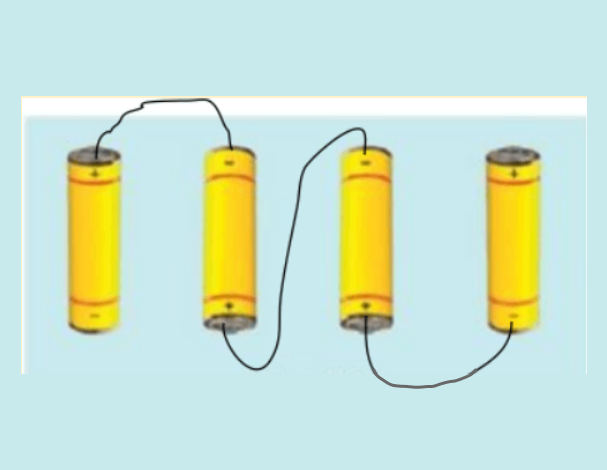
5. What is the correct way to connect cells to form a battery as per NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Solutions?
According to NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 10, cells should be connected such that the negative terminal of one cell is joined to the positive terminal of the next. This forms a battery and ensures proper current flow in the circuit.
6. How does the magnetic effect of electric current explain compass needle deflection near a current-carrying wire?
As per NCERT Solutions for Electric Current and Its Effects, a current-carrying wire generates a magnetic field. When a compass needle is brought near such a wire, the field interacts with the needle, causing it to deflect from its original north-south position.
7. Why should you not replace a fuse with a regular wire in household circuits as explained in NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 10?
A fuse is made of material with a low melting point, so it melts and breaks the circuit when excessive current flows, protecting devices. Regular wire has a higher melting point and may not break; this can lead to hazards like short circuits or fires.
8. What are the functions and practical applications of an electromagnet (as per Class 7 Science NCERT Solutions)?
Electromagnets are coils of wire wound around an iron core that become magnetized when electric current passes through. Their uses include:
- Lifting heavy iron objects in scrap yards.
- Electric bells and telegraphs.
- Various electrical devices and machinery.
9. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 help in understanding the working of an electric bell?
Class 7 Science Chapter 10 explains that an electric bell uses an electromagnet. When current flows, the electromagnet attracts an iron strip, which rings the bell, and simultaneously disconnects the circuit to stop the ringing, showing the application of magnetic effects of electric current.
10. What steps should you follow to troubleshoot a circuit where the bulb does not glow, according to NCERT Class 7 Science Solutions?
If the bulb does not glow, as per NCERT Solutions:
- Check all wire connections for tightness.
- Ensure the cell is not exhausted.
- Verify the bulb is not fused.
- Test the switch functionality.
- Check if the circuit is complete and properly closed.
11. How does the combination of two or more cells affect the current in an electric circuit (Class 7 Science NCERT Solutions)?
Connecting two or more cells in series (positive to negative terminals) increases the total voltage available in the circuit, thus potentially increasing current and enabling devices to function more efficiently, as explained in NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Ch 10.
12. FUQ: What might happen if electromagnetic effects are ignored in daily appliance design?
If electromagnetic effects are ignored, appliances using electric current might not function as intended; safety devices like fuses would fail to protect, motors and bells would not operate, and there could be risks of overheating or magnetic interference, reflecting the importance of these effects as highlighted in the NCERT Solutions Chapter 10.
13. FUQ: How can you distinguish between conductors and insulators using a simple circuit (based on NCERT Solutions)?
According to Class 7 Science Chapter 10 NCERT Solutions, connect the material between a battery and a bulb.
- If the bulb glows, the material is a conductor (allows current to pass).
- If the bulb does not glow, it is an insulator (blocks current).
14. FUQ: Why is understanding proper wiring and circuit diagrams important as recommended in NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science?
Proper wiring and understanding of circuit diagrams help prevent short circuits, ensure safety, and guarantee correct functioning. NCERT Solutions build foundational skills for recognizing and solving practical electrical problems in higher classes and real life.
15. FUQ: What is the significance of learning about the heating effect of current for future scientific understanding (NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science)?
Understanding the heating effect of current is vital, as it forms the basis for devices like toasters, heaters, and fuses, and is foundational for future studies in physics and engineering, as emphasized in NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10.