NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers FREE PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat
1. What is heat as explained in NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3?
Heat is defined as a form of energy that is transferred from a hotter object to a colder one due to a temperature difference. This process continues until both objects reach the same temperature, achieving thermal equilibrium.
2. How do laboratory thermometers and clinical thermometers differ according to class 7 NCERT Solutions?
Laboratory thermometers usually have a wide temperature range and do not feature a kink, while clinical thermometers are designed for measuring human body temperature, have a narrow range, and include a kink to prevent the mercury from falling quickly.
3. According to the Class 7 Science Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions, why is air trapped between layers of clothing during winter?
When multiple layers of clothing are worn, air gets trapped between them. Air is a poor conductor of heat, so it acts as an insulator and reduces heat loss from the body, keeping us warmer in winter.
4. What examples of conductors and insulators does NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 provide?
- Conductors: Copper and iron
- Insulators: Rubber and ceramic
5. Which process allows heat transfer from the Sun to the Earth according to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 3?
Radiation is the process by which heat from the Sun reaches Earth. It does not require any medium for transfer.
6. Why is the outer wall of houses in hot climates often painted white as per NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science?
White surfaces absorb less heat and reflect more sunlight, which helps keep the interiors of houses cooler in hot climates.
7. What is a thermometer according to NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat?
A thermometer is an instrument used to measure temperature. Common thermometers for scientific or domestic use are laboratory, clinical, and digital thermometers.
8. What would happen if an iron ball at 40°C is placed in water at 40°C? (as per NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 3)
No heat transfer will occur between the iron ball and the water because both are at the same temperature; heat flows only when there is a temperature difference.
9. Why are cooking pans usually made with copper bottoms, as explained in Class 7 Science Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions?
Copper is a better conductor of heat than many other metals. Copper bottoms allow for faster and more even heating of cooking pans.
10. How is heat transferred through a metal spoon placed in hot liquid as per Class 7 Science Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions?
Heat is transferred from the hot end of the metal spoon to the cold end by the process of conduction.
11. What is the main difference between conduction and convection as per Class 7 NCERT Solutions?
Conduction transfers heat through direct contact in solids, while convection involves the movement of fluids (liquids or gases) carrying heat as they move from one place to another.
12. According to NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3, can heat be created or destroyed?
Heat cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transferred from one body to another or changed into other forms of energy, as per the Law of Conservation of Energy.
13. Why is a wooden spoon preferred for stirring hot food as per NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 3?
Wood is a poor conductor of heat (an insulator), so its end does not become hot quickly, making it safe to handle while stirring hot foods.
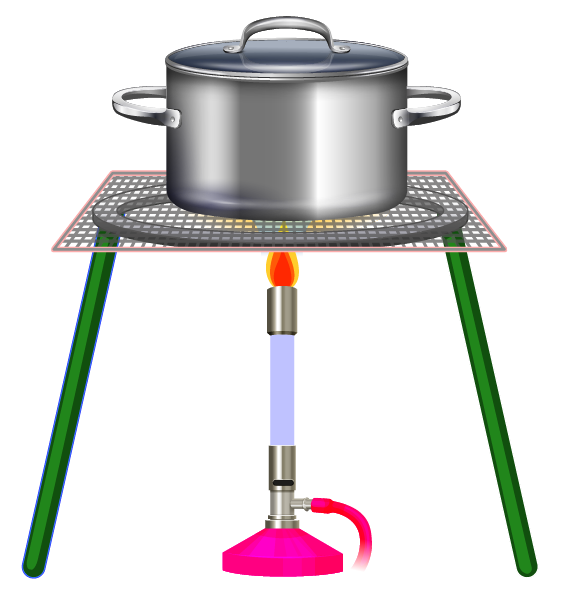
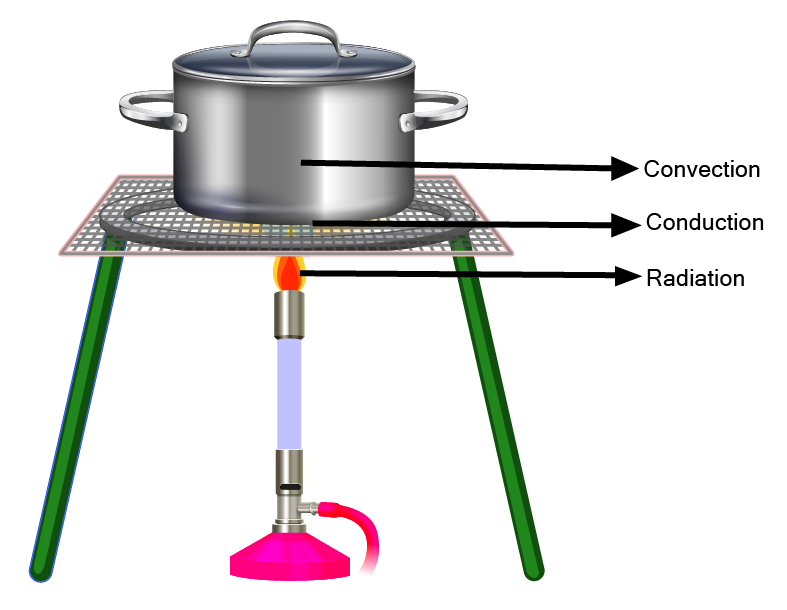
14. What are the key modes of heat transfer explained in NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3?
The three modes of heat transfer are:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
15. How should students use NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 to prepare for exams?
Students should use NCERT Solutions to understand concepts, clarify doubts, and practice the provided stepwise answers so they follow the correct method as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.