NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Forest Our Lifeline Question Answers - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Forest Our Lifeline
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 ‘Forest: Our Lifeline’ and why are they important for exam preparation?
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12 ‘Forest: Our Lifeline’ provide accurate, stepwise answers to all in-text and end-of-chapter textbook questions. As per CBSE 2025–26 guidelines, these solutions help students understand forest ecosystems, the importance of biodiversity, and forest conservation, boosting confidence for exams by clarifying concepts and correct answer-writing formats.
2. How do animals and plants interact in a forest ecosystem, according to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12?
In a forest ecosystem, plants and animals interact in several ways:
- Animals help in seed dispersal, aiding plant growth and the spread of species.
- Plants provide food and shelter to animals.
- Both are interconnected in various food chains, maintaining ecological balance.
- Decomposers break down dead matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil for plants to absorb.
3. Explain why there is minimal waste in a forest as per NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12.
Forests have minimal waste because decomposers (like fungi and bacteria) break down dead plants and animals into humus. This humus enriches the soil and supports new plant growth, ensuring recycling of all organic material within the ecosystem as per CBSE curriculum logic for this chapter.
4. What is the role of decomposers in a forest ecosystem according to Class 7 Science NCERT Solutions?
Decomposers (such as fungi and bacteria) break down dead and decaying matter in forests. They:
- Convert dead plants and animals into humus.
- Release nutrients back into the soil for plant use.
- Help maintain the natural nutrient cycle and fertility of the forest.[CBSE-approved explanation]
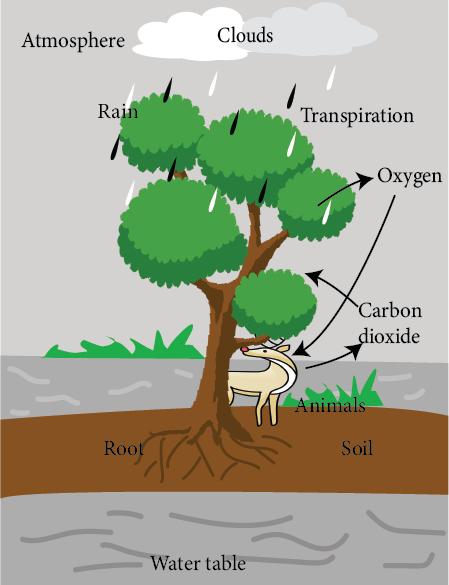
5. How do forests prevent soil erosion and floods as per NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12 solutions?
Forests prevent soil erosion and floods because tree roots bind the soil, making it stable during heavy rains. Canopy cover also reduces the direct impact of rainfall on the soil, helping maintain groundwater levels and preventing floods, as per Class 7 Science NCERT methodology.
6. Why should people care about forests even if they are far from human settlements, according to NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12?
People should care about forests, even distant ones, because forests:
- Regulate the Earth’s climate and oxygen-carbon dioxide balance.
- Support biodiversity, which affects food chains globally.
- Provide essential resources (medicines, wood, etc.) and ecological services benefiting all life, as highlighted in CBSE Class 7 NCERT Solutions.
7. List five key products that humans obtain from forests, as discussed in Class 7 Science Chapter 12.
Important products obtained from forests include:
- Wood
- Honey
- Medicinal herbs
- Rubber
- Oils (such as eucalyptus oil)
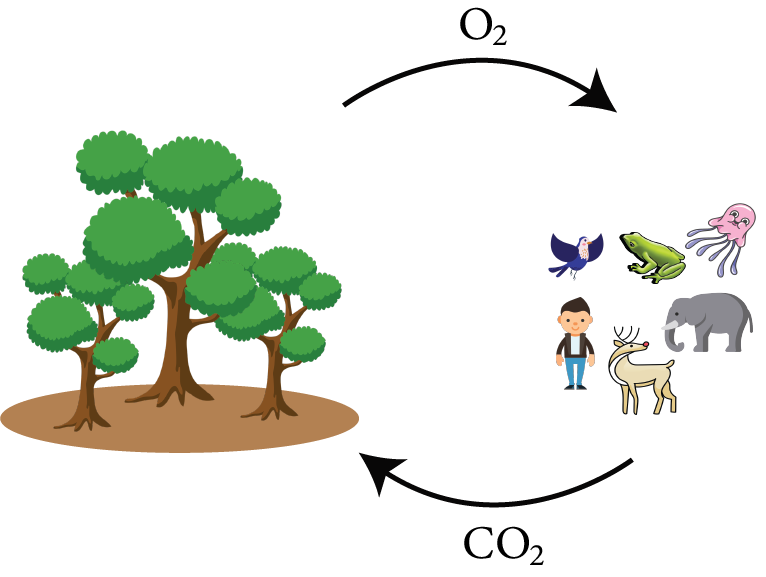
8. How do forests help maintain the oxygen and carbon dioxide balance in the atmosphere?
Forests help maintain the oxygen and carbon dioxide balance by:
- Trees absorb carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and release oxygen.
- Animals breathe oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
- This continuous cycle maintains the atmospheric balance, a key concept in Class 7 NCERT Science.
9. What is humus, and what is its function in the forest ecosystem as per NCERT guidelines?
Humus is the dark, nutrient-rich organic material formed from decomposed plant and animal matter. In forests, it:
- Improves soil fertility.
- Enables better water retention in soil.
- Supports healthy plant growth, supporting the forest’s self-sustaining nature (as per NCERT syllabus for Class 7 Science).
10. Why is biodiversity important in a forest, according to NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12?
Biodiversity sustains complex food chains and the overall stability of a forest. Different animals and plants provide various ecological functions and resources. If any link breaks, the entire food chain and forest health suffer, as explained in CBSE 2025–26 curriculum for "Forest: Our Lifeline".
11. What would happen if forests disappeared, based on learnings from NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12?
If forests disappeared:
- Oxygen levels would decrease, affecting all aerobic life.
- Soil erosion and natural disasters like floods would increase.
- Biodiversity would be lost, resulting in ecosystem collapse.
- Vital resources and climate regulation would be severely impacted, as outlined in NCERT solutions.
12. How are forest layers (canopy, understory, forest floor) different and what are their functions?
The forest canopy is the uppermost layer, formed by leaves and branches, providing shelter and regulating temperature. The understory is below the canopy, consisting of smaller trees and shrubs, offering habitat for different species. The forest floor contains decomposing leaves and organic matter (humus), supporting seed germination and nutrient recycling, as emphasized in class 7 solutions for this chapter.
13. Give one example each of how plants depend on animals and vice versa, as per NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 12.
Plants depend on animals for pollination and seed dispersal (for example, birds spreading seeds). Animals depend on plants for food and oxygen (herbivores eat plants, all animals need oxygen produced by plants). These interdependencies are key syllabus points for "Forest: Our Lifeline".
14. What are the main threats to forests as discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 12?
Main threats to forests include:
- Deforestation for agriculture and urban development.
- Illegal logging and over-exploitation of resources.
- Forest fires and climate change impacts.
15. Why are forests called our lifeline as per Class 7 Science curriculum?
Forests are described as our lifeline because they:
- Support life through oxygen production and air purification.
- Regulate climate and rainfall.
- Provide essential resources and habitats for countless species.