NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 8 Reproduction in Plants Class 7 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Reproduction In Plants
1. What types of questions are answered in the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 8, 'Reproduction in Plants'?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 8 provide complete, step-by-step answers for all questions in the textbook exercise. This includes:
- Fill in the blanks
- Multiple-choice questions (MCQs)
- Match the following
- Short and long descriptive answer questions
Each solution is crafted to align with the CBSE 2025-26 curriculum guidelines.
2. How do the NCERT Solutions correctly explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination?
The solutions clarify this by first defining each term and then often presenting the differences in a simple table. It explains that self-pollination involves the transfer of pollen to the stigma of the same flower, whereas cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen to the stigma of another flower of the same kind. This method helps students compare and remember the distinct mechanisms easily.
3. What is the correct method shown in the solutions for answering questions on asexual reproduction methods like budding or fragmentation?
The NCERT solutions demonstrate the correct method by first defining the specific type of asexual reproduction and then providing a mandatory example. For instance, when explaining budding, the answer describes the formation of a bud-like projection from the parent cell and cites yeast as an example. This 'definition plus example' approach is crucial for scoring full marks.
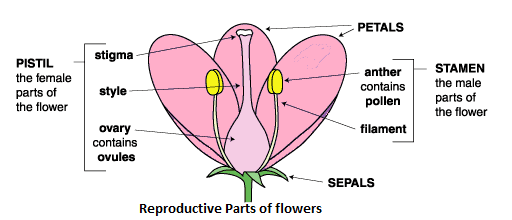
4. Why do the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 8 emphasize drawing and labelling a diagram for the reproductive parts of a flower?
Drawing a labelled diagram is emphasized because it is a key requirement for questions on plant structures as per the CBSE pattern. A diagram visually demonstrates your understanding of the parts and their positions. The solutions show how to correctly draw and label the male part (stamen) and the female part (pistil), which helps secure higher marks than a purely text-based answer.
5. How do the solutions help in understanding the sequence of events from fertilisation to fruit formation?
The solutions explain this as a step-by-step process. They clarify that after fertilisation (the fusion of male and female gametes), the resulting zygote develops into an embryo. The ovule then develops into a seed, and the ovary matures and transforms into a fruit. By laying out this sequence, the solutions help students understand the entire post-fertilisation life cycle logically.
6. Beyond providing answers, how do these solutions clarify the role of dispersal agents like wind, water, and animals?
The solutions go beyond simple lists by linking each agent to the type of seed it disperses. For example, they explain that light, winged seeds (like those of maple) are adapted for wind dispersal, while seeds with fibrous or spongy outer coats (like coconut) are suited for water dispersal. This helps students understand the relationship between a seed's structure and its dispersal mechanism.
7. Are the methods and terminology used in these NCERT Solutions aligned with the 2025-26 academic session?
Yes, all explanations, definitions, and problem-solving methods in the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 8 are fully updated and accurate as per the latest CBSE syllabus for the 2025-26 session. The answers are designed by experts to ensure students learn the precise terminology and concepts required for their exams.